Sustained uremic toxin control improves renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with advanced renal dysfunction: post-hoc analysis of the Kremezin Study against renal disease progression in Korea [Volume 36, Issue 1, March 2017, Pages 68–78]
Article information
The above article (https://doi.org/10.23876/j.krcp.2017.36.1.68) contains errors.
The values of y axis in Fig. 3 should be corrected as following page.
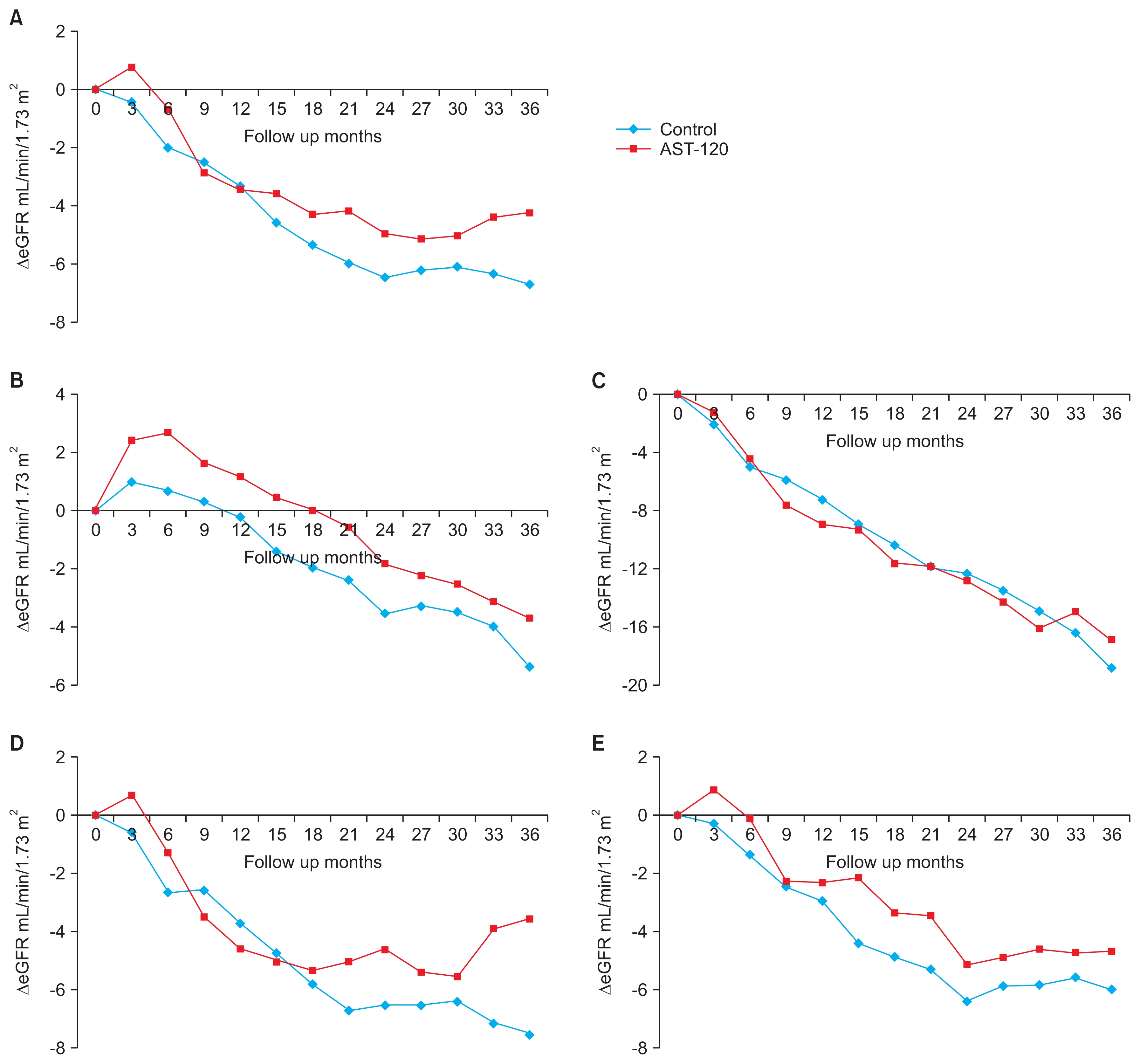
Change of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) over time
(A) From whole per-protocol participants (Prandomization = 0.18, Prandomization-time = 0.04). (B) From participants without a composite primary outcome (Prandomization = 0.01). (C) From participants with a composite primary outcome (Prandomization = 0.28). (D) From participants with diabetic nephropathy (Prandomization = 0.54, Prandomization-time = 0.049). (E) From participants with non-diabetic nephropathy (Prandomization = 0.21).
The authors would like to apologize for any inconvenience this has caused.