| Kidney Res Clin Pract > Volume 37(4); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background
Nephrotic syndrome (NS) is the most common glomerulopathy in children. Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication of NS, caused by severe intravascular volume depletion, acute tubular necrosis, interstitial nephritis, or progression of NS. However, the incidence and risk factors of childhood-onset NS in Korea are unclear. Therefore, we studied the incidence, causes, and risk factors of AKI in hospitalized Korean patients with childhood-onset NS.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective review of patients with childhood-onset NS who were admitted to our center from January 2015 to July 2017. Patients with decreased renal function or hereditary/secondary NS, as well as those admitted for management of other conditions unrelated to NS, were excluded.
Results
During the study period, 65 patients with idiopathic, childhood-onset NS were hospitalized 90 times for management of NS or its complications. Of these 90 cases, 29 met the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes criteria for AKI (32.2%). They developed AKI in association with infection (n = 12), NS aggravation (n = 11), dehydration (n = 3), and intravenous methylprednisolone administration (n = 3). Age ≥ 9 years at admission and combined use of cyclosporine and renin-angiotensin system inhibitors were risk factors for AKI.
Conclusion
AKI occurred in one-third of the total hospitalizations related to childhood-onset NS, owing to infection, aggravation of NS, dehydration, and possibly high-dose methylprednisolone treatment. Age at admission and use of nephrotoxic agents were associated with AKI. As the AKI incidence is high, AKI should be considered during management of high-risk patients.
Nephrotic syndrome (NS) is the most common glomerular kidney disease in children [1–5]. It is often complicated by infections, thromboembolism, hypovolemic crisis, and acute kidney injury (AKI). AKI is generally known to be associated with high mortality and morbidity, including risk of progression to chronic kidney disease [6–12]. AKI in children with NS is believed to be a consequence of severe intravascular volume depletion, acute tubular necrosis, interstitial nephritis, or rapid progression of the original glomerular or genetic disease of the patient [13]. Compared with other complications of NS, AKI is considered relatively uncommon, with a reported incidence of < 1% to 34% of the total pediatric population with NS in earlier studies [2,14,15]. In contrast, a recent study showed an AKI incidence of 51% in hospitalized children [9,16]. Such a difference in AKI incidence implies that the current knowledge of this NS complication is insufficient. Furthermore, there has been no comprehensive report on the incidence and risk factors of AKI in patients with childhood-onset NS in Korea.
To enhance current knowledge, we investigated the incidence, causes, and risk factors of AKI in hospitalized patients with childhood-onset idiopathic NS in Korea.
This was a single-center, retrospective study at a tertiary referral hospital in South Korea. This study was approved by the institutional review board of Seoul National University Hospital (No. 1602-010-739). Diagnosis, remission, and relapse of idiopathic NS were defined according to the International Classification of Disease, 10th revision of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (https://www.cdc.gov). Records of all hospitalized patients with childhood-onset NS at our center between January 1, 2015 and July 31, 2017 were reviewed. Patients were excluded if 1) diagnosed as hereditary NS or NS secondary to other systemic diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, Henoch-Schölein purpura, or immunoglobulin A nephropathy; 2) diagnosed with chronic kidney disease stage II or higher; 3) glomerulonephritis or other uncertain findings were found pathologically; 4) admitted for elective kidney biopsy or infusion of prescheduled intravenous methylprednisolone or rituximab; or 5) admitted for management of other conditions not related to NS. Age limitation was not applied. The remaining patients admitted for treatment of NS or its complications were included in this study. Data on patient characteristics, reasons for admission, and medications administered on or during admission were obtained. Moreover, medication history of cyclosporine (CyA), tacrolimus, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs), angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), intravenous methylprednisolone, and oral or intravenous antibiotics was collated.
AKI was defined according to the 2012 Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) AKI guidelines as increase in serum creatinine level to ≥ 1.5 times the baseline level or increase in serum creatinine level by ≥ 0.3 mg/dL within 48 hours [17]. The serum creatinine measurements at our institution are reported as isotope dilution mass spectrometry-traceable values. Baseline creatinine level was defined as the lowest creatinine value obtained during the 3-month period before admission. If this value was not available, the lowest creatinine value obtained during admission was considered the baseline creatinine level of the patient. If the highest value of serum creatinine level during an episode was < 0.5 mg/dL, that episode was not considered to be AKI, as described in an earlier pediatric study [18]. The estimated glomerular filtration rate was calculated using the bedside Schwarz formula (0.413 × height/serum creatinine value; in mL/min per 1.73 m2) [19–22].
With respect to causes of AKI, we attempted to find 1 main cause per case by reviewing the medical records for symptoms and signs. Many patients had more than 1 condition, including infection, dehydration, and aggravation of NS, at the same time. However, only those with clear evidence of significant infection when AKI developed, such as high C-reactive protein level and requirement for antibiotics, were considered to have infection as their main cause of AKI. Dehydration was considered the main cause of AKI when evidence of significant infection was not present and symptoms of diarrhea, vomiting, and/or decreased intake were evident. NS aggravation was chosen as the main cause of AKI when patients had no evidence of infection or dehydration but had signs and symptoms of NS, namely sudden body weight increase or relapse of proteinuria.
Data are expressed as frequencies, percentages, median values, and interquartile ranges. Hospitalization cases that were complicated with AKI formed the AKI group, and all other hospitalization cases made up the non-AKI group. The two groups were compared using non-parametric statistical tests including chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, and Mann–Whitney U test. The relationships between AKI and its risk factors were analyzed using a multivariate logistic regression model including binary variables with a P < 0.05 in chi-square testing and other variables of interest. All analyses were performed using SPSS, version 23 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). A P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
A total of 166 patients with childhood-onset NS were hospitalized 381 times during the study period. Of these, 100 hospitalizations of 32 patients with hereditary or secondary NS and chronic kidney disease were excluded. Among the remaining 281 hospitalizations of 134 patients, prescheduled hospitalizations for intravenous medication of methylprednisolone or rituximab (n = 130) or hospitalizations not related to NS (n = 61) were excluded. Finally, a total of 90 hospitalizations of 65 patients (male-to-female ratio 44:21) were included in this study. The pathologic diagnoses of the subjects were minimal change disease in 20 (30.8%), focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in 7 (10.8%), and C1q nephropathy in 2 (3.1%). Of the 65 patients, 46 responded to initial steroid therapy (steroid-sensitive NS) and 19 did not (steroid-resistant NS); 16 patients were frequent relapsers (frequent-relapse NS) and 48 were infrequent relapsers (infrequent-relapse NS).
At hospitalization (n = 90), the median age of the patients was 7.8 years (interquartile range, 4.4–14.3 years). A total of 64.6% of the hospitalizations were for management of NS itself, and the rest were for management of NS complications. The most common reason for admission was infection (n = 43, 47.8%; upper respiratory infection [URI] in 11, acute gastroenteritis in 10, URI with acute gastroenteritis in 5, influenza in 4, acute otitis media in 3, pneumonia in 3, sepsis in 3, peritonitis in 2, viral meningitis in 1, and cellulitis in 1 patient), followed by NS aggravation (n = 39, 43.3%) and dehydration including hypovolemic crisis (n = 8, 8.9%). There were no cases of thromboembolism in our study population during the study period.
AKI occurred in a total of 29 hospitalizations (32.2%) of 26 patients, with a median AKI onset of 0 days after admission (range, 0–10 days). When the 2012 KDIGO AKI guidelines were applied, the highest stage of AKI was I in 11 (37.9%), II in 7 (24.1%), and III in the remaining (37.9%) AKI cases. The median resolution time of the AKI episodes was 7 days (range, 1–27 days). None of the patients required renal replacement therapy or intensive care, and there was no mortality. The causes of AKI were infection in 12 (41.4% of the AKI group), NS aggravation in 11 (37.9%), and dehydration in 3 (10.3%) cases, whereas there was no identifiable cause of AKI other than high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone administration in 3 (10.3%) cases (Fig. 1).
Comparing the AKI and non-AKI groups, patients in the AKI group were older than those in the non-AKI group (P = 0.007) (Fig. 2). However, no statistically significant differences were observed between the AKI and non-AKI groups in sex; age at onset of NS; pathologic diagnosis; duration of NS; sensitivity to initial steroid therapy (steroid-sensitive NS vs. steroid-resistant NS) or relapse type (frequent-relapse NS vs. infrequent-relapse NS); reason for admission; use of CyA, tacrolimus, ACEIs, ARBs, methylprednisolone, or antibiotics during admission; number of relapses during the previous admission year; or body weight gain (%) on admission (Table 1). Patients using CyA and ACEIs or ARBs (renin-angiotensin system inhibitor [RASi]) were more common in the AKI group. To investigate the risk factors for AKI, we a priori selected sex, steroid-resistant NS, medications (CyA, tacrolimus, RASi, and methylprednisolone), and infection based on a literature review. The significantly different variables between the AKI group and non-AKI group (age ≥ 9 years at admission and CyA + RASi) were included in the multivariate regression model are were associated with AKI (P = 0.008, odds ratio [OR], 3.783; P = 0.018, OR, 3.440, respectively; Table 2).
With respect to the laboratory findings, the serum levels of albumin and cholesterol at the time of admission, proteinuria (urine protein/creatinine ratio, in mg/mg) at admission, and trough level of calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs) were not statistically significantly different between the AKI and non-AKI groups. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN; 32 vs. 12 mg/dL) and uric acid (7.8 vs. 5.7 mg/dL) levels at admission were significantly higher in the AKI group than in the non-AKI group. The uric acid level was higher in the AKI group than in the non-AKI group throughout the admission period, with a median uric acid level of 6.7 mg/dL (vs. 5.3 mg/dL in the non-AKI group, P < 0.001).
The hospitalization duration was longer in the AKI group (median of 12 days vs. 6 days in the non-AKI group, P = 0.002) (Table 1).
Of the 29 AKI hospitalizations, there were 3 cases of AKI development or aggravation with high-dose intravenous glucocorticosteroid administration. All of those patients were males and were taking CNIs and ACEIs. The pathologic diagnosis was minimal change disease in all 3 cases, and their lengths of stay were comparatively longer than the median hospital days of others with AKI (21, 80, and 28 days in the methylprednisolone-induced AKI cases vs. 7 days in other AKI cases). The 3 admissions were all associated with infection (URI, influenza, and sinusitis, respectively) at admission; however, only 2 patients had been prescribed oral and intravenous antibiotics (P2 and P3) (Table 3). With resolution of infection, high-dose steroid therapy was used to manage refractory NS. The patients showed a sudden increase in creatinine level after administration of high-dose (30 mg/kg) methylprednisolone, and discontinuation of methylprednisolone along with supportive care resulted in recovery of renal function (Fig. 3). The characteristics of these 3 cases did not differ from those of the other 22 non-AKI hospitalization cases in which methylprednisolone was also administered (data not shown).
In our study, one-third (32.2%) of childhood-onset NS hospitalizations were complicated by AKI. Compared with some earlier studies reporting an AKI incidence as low as < 10% in pediatric NS [23,24], the AKI incidence in our study is much higher. However, recent studies have shown that the AKI incidence in idiopathic NS has increased [1,2,9]. Rheault et al [1] found that 50.9% of NS hospitalizations were complicated by any pRIFLE (Pediatric Risk, Injury, Failure, Loss, End stage renal disease) stage of AKI in a multicenter study. Compared with their study, we found a lower incidence of AKI. The higher AKI incidence may partly stem from a greater awareness of AKI and application of the KDIGO guideline criteria. Another explanation may be related to a selection bias, as our study was conducted at a tertiary hospital with a high concentration of patients with more severe NS and where many of the patients were aggressively treated with CNIs and RASis. CNIs and RASis are well-known nephrotoxic agents [1,25], as supported in our study. Nevertheless, the high AKI incidence is concerning, and close monitoring is needed to appropriately treat patients with AKI especially in the early period of hospitalization considering that the median onset of AKI was day 0 of hospitalization. As expected, our study found longer hospital stays in the AKI group than in the non-AKI group (median 12 vs. 6 days, P = 0.002), which would result in higher medical costs and increased possibility of hospital-acquired infections and other related complications [1,2,16].
The etiology of AKI in NS includes pre-renal AKI with intravascular volume depletion; exposure to nephrotoxic medications including CNIs, ACEIs, ARBs, and antibiotics; acute tubular necrosis; sepsis; renal vein thrombosis; and infections such as peritonitis and interstitial nephritis [26]. In our study, the most probable causes of AKI were infections and intravascular volume depletion associated with aggravation of NS and dehydration. As all of our patient admissions were for management of NS or NS complications, it can be assumed that most of the patients had volume depletion to some degree. With respect to nephrotoxic medications [1,2,27], 56.7% of our cases were treated with CNIs, 66.7% with RASis, and 22.2% with antibiotics. Statistical analysis showed that CyA in combination with RASi was associated with AKI (Table 1). CNIs and RASi are known to decrease glomerular perfusion; therefore, using these medications in situations with intravascular volume depletion would lead to AKI. Therefore, precautions should be taken when administering these medications to patients with NS.
The comparison of characteristics revealed that patients in the AKI group were older at hospitalization than those in the non-AKI group (median, 11.3 vs. 7.1 years). Other characteristics, except for medication, were not different between the two groups. Multivariate analysis showed similar results, indicating that age ≥ 9 years at admission was significantly related to AKI. Our study is limited by the small number of subjects and the inclusion of non-pediatric patients (n = 8), which might have biased the results. Nonetheless, we speculate that the poor compliance of adolescents or the rapid changes in metabolism associated with this period of development, along with possible over- or under-dosage of medication for the physiology of the patients, may have been contributing factors. A similar finding was observed in an earlier study showing that patients aged > 9 years had higher ORs of AKI incidence than younger patients, but without statistical significance [1]. In contrast, previous studies found steroid-resistant NS to be a risk factor of AKI [1,28], whereas our study found that initial response to steroid and pathologic diagnosis were not statistically significant. In a comprehensive multicenter study by Rheault et al [1], non-white race and presence of infection were found to be additional risk factors for AKI along with nephrotoxic medications (number, duration, and intensity). As our study has the shortcomings of being a small, retrospective, single-center study, a large-scale multicenter study is needed to clarify the significance of our findings.
With respect to the laboratory results, the serum uric acid and BUN levels at the time of admission were higher in the AKI group (uric acid 7.8 vs. 5.7 mg/dL, BUN 32 vs. 12 mg/dL; P < 0.001 for both), whereas the serum albumin levels were not different between the two groups (1.8 vs. 1.9 g/dL, P = 0.582). Although high uric acid and BUN levels are expected findings in AKI, they might also indicate more severe volume depletion in these patients. The tendency of higher uric acid level in the AKI group was also observed over the 12 months before admission (data not shown), in addition to at admission. This finding raises the question of whether patients with higher uric acid level are more prone to AKI. As hyperuricemia is known to cause renal injury through crystal formation or reactive oxygen radical production and inflammatory mediator-related mechanisms [29–31], the answer might be yes; however, further studies are needed to answer this question with certainty.
Interestingly, we observed AKI aggravation and/or development along with high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone therapy in 3 cases. Although methylprednisolone pulse therapy is a well-known treatment for children with steroid-resistant NS [32–36], some studies reported that this medication induces AKI. Sakemi et al [37,38] reported that 3 of 25 patients who received methylprednisolone pulse therapy experienced progressive deterioration of renal function, with recovery of renal function on discontinuation of methylprednisolone. They found that hypoproteinemia was the most important index for differentiation between the AKI and non-AKI groups among patients receiving methylprednisolone pulse therapy. However, in our study, serum albumin level was not lower in AKI cases (1.8, 1.9, and 2.9 g/dL) than in the other 22 non-AKI cases with methylprednisolone treatment. The mechanism of methylprednisolone-induced AKI is still unclear, although sodium and water retention similar to mineralocorticoid and interstitial edema has been proposed, rather than tubular necrosis [37,39]. Renal histology was not obtained for our study cases at the time of AKI; consequently, we have no knowledge of any possible tubular damage involvement. Nevertheless, as was the case in earlier studies, all 3 patients in our study recovered from AKI after discontinuation of high-dose methylprednisolone administration. Physicians should be aware that methylprednisolone pulse therapy could be associated with AKI in some patients, although the condition is reversible with cessation of medication. Thus, close observation and monitoring are necessary for patients undergoing high-dose glucocorticoid therapy.
In conclusion, the incidence of AKI in hospitalized Korean patients was rather high at > 30%. The main causes of AKI were infection, NS aggravation, dehydration, and possibly high-dose methylprednisolone therapy. Older age at admission and combined use of CyA and RASi were found to be risk factors in hospitalized Korean patients with childhood-onset NS. As the AKI incidence is high, AKI should be considered during management of such patients, especially when they are treated with CNIs and RASis. Furthermore, most AKI cases were incidentally diagnosed at the time of admission, and close observation and monitoring are needed especially in the early period of hospitalization.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grant no. 2520160020 from the Seoul National University Hospital Research Fund.
Figure 1
Causes of acute kidney injury (AKI) complicating hospitalization of patients with childhood-onset nephrotic syndrome.
AKI occurred in 32.2% of hospitalizations related to childhood-onset nephrotic syndrome (NS) during the study period. The most common cause of AKI was infection (n = 12), followed by aggravation of NS (n = 11), dehydration (n = 3), and possibly high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone (mPD) treatment (n = 3).

Figure 2
Age distribution between groups according to the Mann–Whitney U test.
It showed that patients in the acute kidney injury (AKI) group were older at admission than those in the non-AKI group (median age, 11.3 vs. 7.1 years; P = 0.007). However, there were no statistically significant differences in age at onset (P = 0.054) or duration of illness (P = 0.117).
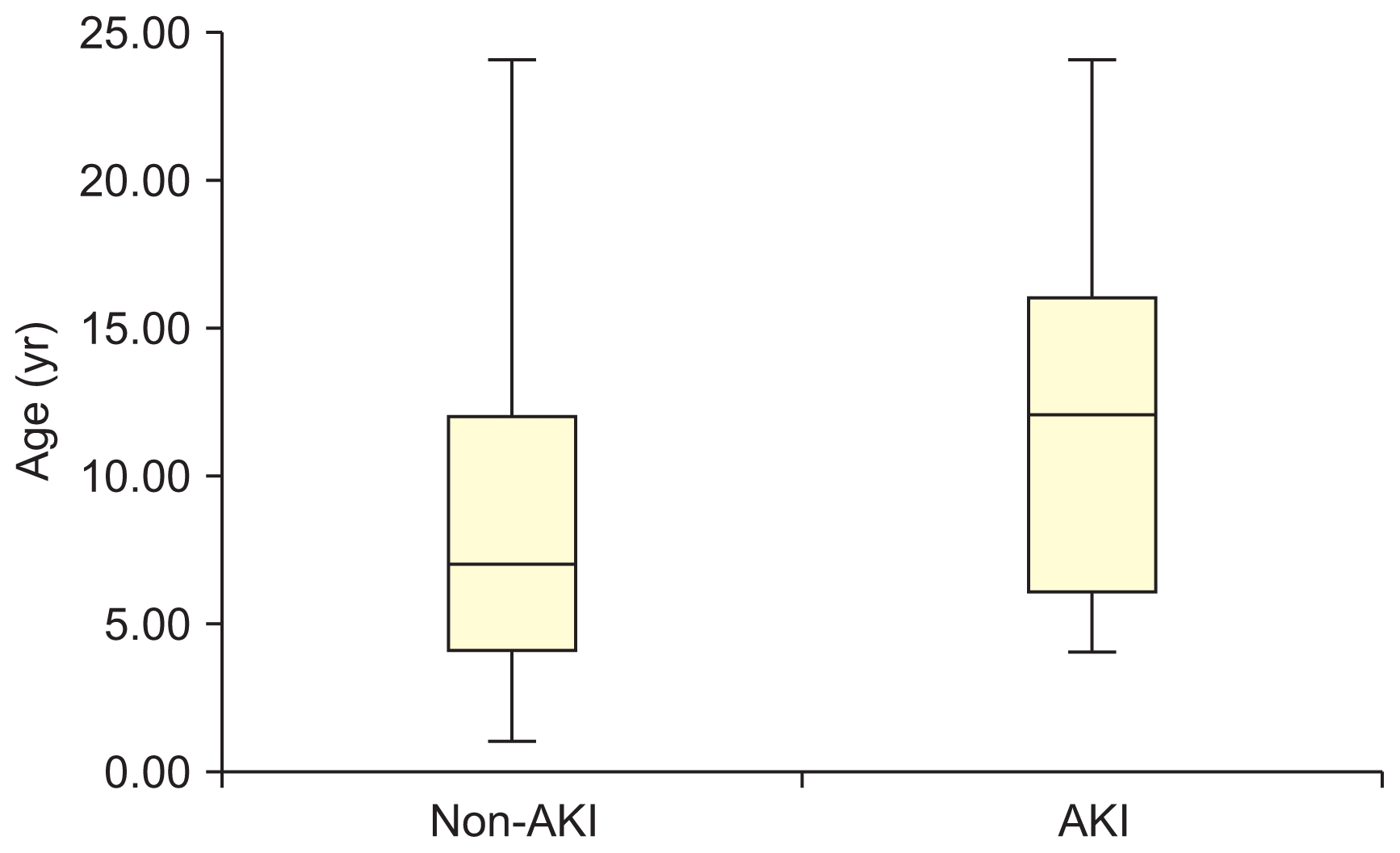
Figure 3
Creatinine trend in patients with acute kidney injury that was possibly associated with methylprednisolone.
(Arrows mean methylprednisolone pulse therapy.) (A) Patient 1, (B) patient 2, (C) patient 3. Three patients showed acute kidney injury aggravation and/or development with high-dose intravenous methylprednisolone administration. With supportive care and discontinuation of methylpredniso-lone, all three recovered to baseline creatinine level.
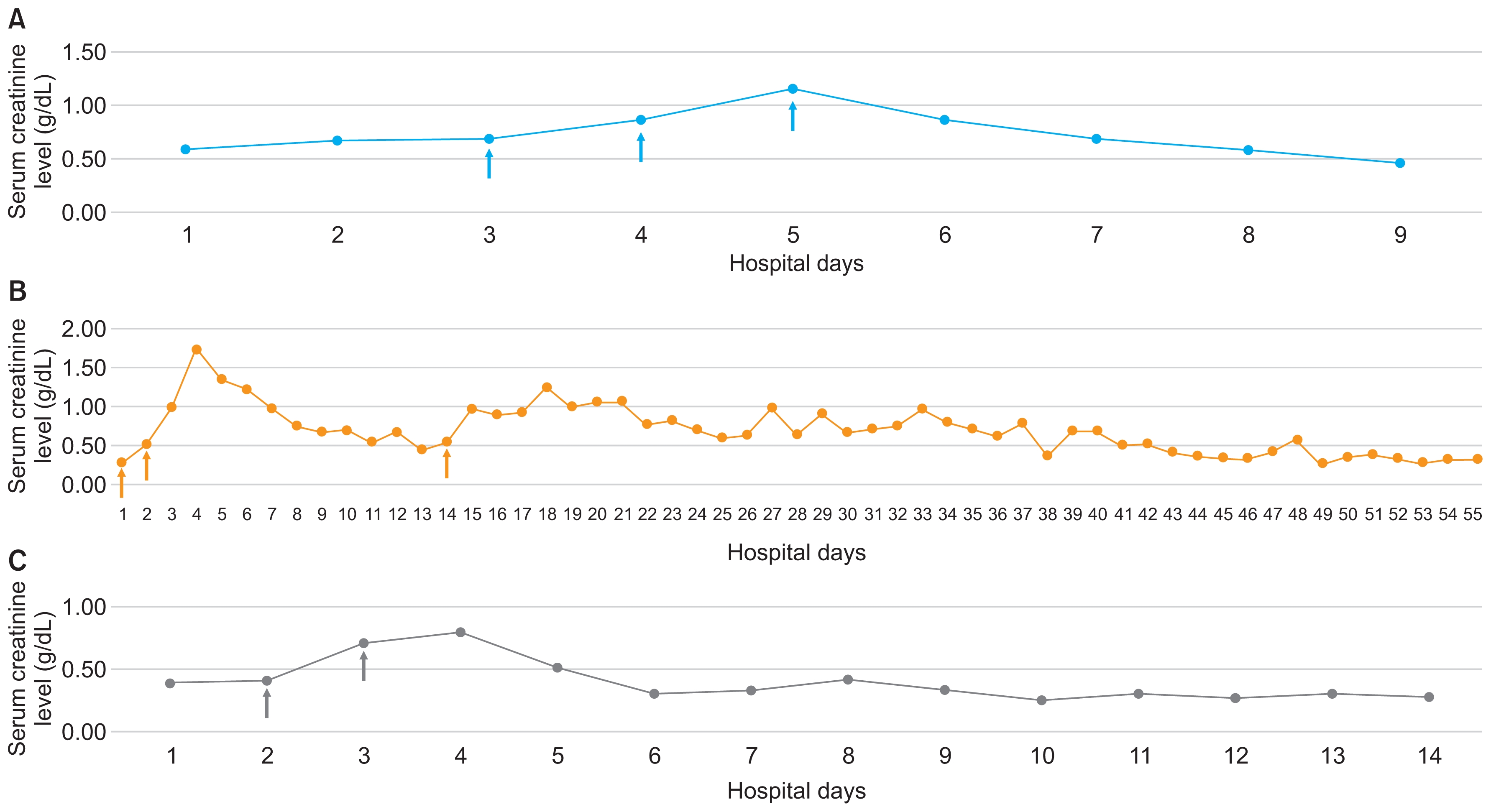
Table 1
Patient characteristics and clinical data during admission: AKI group vs. non-AKI group
| Variable | AKI (n = 29 hospitalizations) | Non-AKI (n = 61) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, male:female | 22:7* | 37:24* | 0.156† |
| Age at admission (yr) | 11.3 (6.7–16.0) | 7.1 (4.1–12.3) | 0.007‡ |
| Onset age (yr) | 5.6 (2.9–9.2) | 4.0 (2.6–6.6) | 0.054‡ |
| Duration of illness (mo) | 42 (6–74.5) | 17 (0–50.5) | 0.117‡ |
| Pathologic findings | 0.944† | ||
| MCD | 17 (58.6) | 15 (24.6) | |
| FSGS | 3 (10.3) | 5 (8.2) | |
| C1q | 1 (3.4) | 2 (3.3) | |
| Others (including “not done”) | 8 (27.7) | 39 (63.9) | |
| Medications on or during admission | |||
| CyA | 16 (55.2) | 24 (39.3) | 0.158† |
| Tacrolimus | 5 (17.2) | 8 (13.1) | 0.603† |
| ACEIs | 17 (58.6) | 33 (54.1) | 0.687† |
| ARBs | 4 (13.8) | 6 (9.8) | 0.577† |
| Methylprednisolone | 11 (37.9) | 14 (23.0) | 0.138† |
| Antibiotics (PO or IV) | 7 (24.1) | 13 (21.3) | 0.763† |
| Medications during admission, combined | |||
| RASi | 22 (75.9) | 39 (63.9) | 0.425† |
| CyA with RASi | 12 (41.4) | 15 (24.6) | 0.034† |
| Tacrolimus with RASi | 5 (17.2) | 7 (11.5) | 0.513† |
| CyA or tacrolimus with RASi | 15 (41.4) | 22 (36.1) | 0.062† |
| Reason for admission | 0.721† | ||
| Deterioration of NS | 15 (51.7) | 34 (55.7) | |
| Complication of NS | 14 (48.3) | 27 (44.3) | |
| Evidence of infection (+) | 14 (48.3) | 28 (45.9) | 0.833† |
| Evidence of dehydration (+) | 3 (10.3) | 5 (8.2) | 0.738† |
| Initial response | 0.280† | ||
| Sensitive to steroid | 22 (75.9) | 41 (67.2) | |
| Resistant to steroid | 7 (24.1) | 20 (32.8) | |
| Relapse pattern§ | 0.403† | ||
| Frequent relapse | 5 (17.2) | 17 (27.9) | |
| Infrequent relapse | 24 (82.8) | 43 (72.1) | |
| Relapse number | 1 (0–3) | 1 (0–3) | 0.470‡ |
| Body weight difference (%) | 11.3 (4.9–17.6) | 6.9 (3.3–15.2) | 0.179‡ |
| Serum albumin at admission (g/dL) | 1.8 (1.6–2.1) | 1.9 (1.6–2.2) | 0.582‡ |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | |||
| Uric acid at admission | 7.8 (6.5–8.9) | 5.7 (4.5–6.9) | <0.001‡ |
| Uric acid during admission | 6.7 (3.2–7.7) | 5.3 (4.3–6.3) | <0.001‡ |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dL) | 32 (14.5–41) | 12 (9.5–19) | <0.001‡ |
| Urine P/Cr ratio | 12.0 (8.6–19.3) | 14.9 (7.0–31.0) | 0.796‡ |
| Drug level (−7 to +7 d of admission) | |||
| CyA (ng/mL) | 87.8 (46.6–119.4) | 72.3 (40.2–106.6) | 0.706‡ |
| Tacrolimus (ng/mL) | 5.9 (3.5–7.9) | 6.1 (4.0–7.9) | 0.950‡ |
| Duration of admission (d) | 12 (5.5–19) | 6 (3.5–13.5) | 0.002‡ |
ACEI, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; AKI, acute kidney injury; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; C1q, C1q nephropathy; CyA, cyclosporine; FSGS, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis; IV, intravenous; MCD, minimal change disease; NS, nephrotic syndrome; P/Cr, protein/creatinine; PO, oral; RASi, renin-angiotensin system inhibitor.
Table 2
Risk factors associated with acute kidney injury*
| Category | P value* | OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.112 | 2.358 (0.818–6.802) |
| Age, ≥ 9 yr | 0.008 | 3.783 (1.416–10.103) |
| SRNS | 0.216 | 0.453 (0.129–1.588) |
| Medication | ||
| CyA | 0.887 | 1.145 (0.178–7.359) |
| Tacrolimus | 0.265 | 2.344 (0.524–10.494) |
| RASi | 0.407 | 0.588 (0.168–2.061) |
| CyA with RASi | 0.018 | 3.440 (1.235–9.578) |
| Methylprednisolone | 0.239 | 2.087 (0.614–7.095) |
| Evidence of infection | 0.964 | 0.975 (0.328–2.897) |
Table 3
Characteristics of patients with acute kidney injury associated with methylprednisolone pulse (mPD) therapy
References
1. Rheault MN, Zhang L, Selewski DT, et al. AKI in children hospitalized with nephrotic syndrome. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 10:2110–2118. 2015;



2. Rheault MN, Wei CC, Hains DS, Wang W, Kerlin BA, Smoyer WE. Increasing frequency of acute kidney injury amongst children hospitalized with nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 29:139–147. 2014;


3. Gipson DS, Massengill SF, Yao L, et al. Management of childhood onset nephrotic syndrome. Pediatrics 124:747–757. 2009;


4. Huh J, Choi Y, Cheong HI, Ha IS. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis in nephrotic children. Korean J Nephrol 13:832–840. 1994.
5. Hong IH, Go CW, Goo JH, et al. Long term cyclosporine A (Cypol®) therapy in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Korean J Nephrol 20:242–249. 2001.
6. Askenazi DJ, Feig DI, Graham NM, Hui-Stickle S, Goldstein SL. 3–5 year longitudinal follow-up of pediatric patients after acute renal failure. Kidney Int 69:184–189. 2006;


7. Goldstein SL, Devarajan P. Pediatrics: acute kidney injury leads to pediatric patient mortality. Nat Rev Nephrol 6:393–394. 2010;


8. Mammen C, Al Abbas A, Skippen P, et al. Long-term risk of CKD in children surviving episodes of acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit: a prospective cohort study. Am J Kidney Dis 59:523–530. 2012;


9. Yaseen A, Tresa V, Lanewala AA, et al. Acute kidney injury in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome of childhood is a major risk factor for the development of chronic kidney disease. Ren Fail 39:323–327. 2017;



10. Zagury A, Oliveira AL, Montalvão JA, et al. Steroid-resistant idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children: long-term follow-up and risk factors for end-stage renal disease. J Bras Nefrol 35:191–199. 2013;


11. Hamasaki Y, Yoshikawa N, Nakazato H, et al. Prospective 5-year follow-up of cyclosporine treatment in children with steroid-resistant nephrosis. Pediatr Nephrol 28:765–771. 2013;


12. Furuya R, Kumagai H, Ikegaya N, et al. Reversible acute renal failure in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Intern Med 32:31–35. 1993;


13. Koomans HA. Pathophysiology of acute renal failure in idiopatic nephrotic syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16:221–224. 2001;


14. Susantitaphong P, Cruz DN, Cerda J, et al. World incidence of AKI: a meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 8:1482–1493. 2013;



15. Nawaz S, Afzal K. Pediatric acute kidney injury in North India: a prospective hospital-based study. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 29:689–697. 2018;


16. Sutherland SM, Byrnes JJ, Kothari M, et al. AKI in hospitalized children: comparing the pRIFLE, AKIN, and KDIGO definitions. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 10:554–561. 2015;



17. KDIGO Guidelines 2012 Available at: https://kdigo.org/guidelines. Date accessed: March 2018.
18. Kaddourah A, Basu RK, Bagshaw SM, Goldstein SL. AWARE Investigators. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill children and young adults. N Engl J Med 376:11–20. 2017;


19. Staples A, LeBlond R, Watkins S, Wong C, Brandt J. Validation of the revised Schwartz estimating equation in a predominantly non-CKD population. Pediatr Nephrol 25:2321–2326. 2010;


20. Schwartz GJ, Muñoz A, Schneider MF, et al. New equations to estimate GFR in children with CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:629–637. 2009;



21. Hogg RJ, Furth S, Lemley KV, et al. National Kidney Foundation’s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease in children and adolescents: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Pediatrics 111:1416–1421. 2003;


22. Schwartz GJ, Haycock GB, Edelmann CM Jr, Spitzer A. A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in children derived from body length and plasma creatinine. Pediatrics 58:259–263. 1976;


23. Kiliś-Pstrusińska K, Zwolińska D, Musiał K. Acute renal failure in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pol Merkur Lekarski 8:462–464. 2000 In Polish.
24. Gipson DS, Messer KL, Tran CL, et al. Inpatient health care utilization in the United States among children, adolescents, and young adults with nephrotic syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis 61:910–917. 2013;


25. Meyrier A, Niaudet P. Acute kidney injury complicating nephrotic syndrome of minimal change disease. Kidney Int 94:861–869. 2018;


26. Smith JD, Hayslett JP. Reversible renal failure in the nephrotic syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis 19:201–213. 1992;


27. Agarwal N, Phadke KD, Garg I, Alexander P. Acute renal failure in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 18:1289–1292. 2003;


28. Beins NT, Dell KM. Long-term outcomes in children with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome treated with calcineurin inhibitors. Front Pediatr 3:1042015;



29. Xu X, Hu J, Song N, et al. Hyperuricemia increases the risk of acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol 18:272017;



30. Otomo K, Horino T, Miki T, et al. Serum uric acid level as a risk factor for acute kidney injury in hospitalized patients: a retrospective database analysis using the integrated medical information system at Kochi Medical School Hospital. Clin Exp Nephrol 20:235–243. 2016;


31. Hahn K, Kanbay M, Lanaspa MA, Johnson RJ, Ejaz AA. Serum uric acid and acute kidney injury: a mini review. J Adv Res 8:529–536. 2017;


32. Kirpekar R, Yorgin PD, Tune BM, Kim MK, Sibley RK. Clinicopathologic correlates predict the outcome in children with steroid-resistant idiopathic nephrotic syndrome treated with pulse methylprednisolone therapy. Am J Kidney Dis 39:1143–1152. 2002;


33. Griswold WR, Tune BM, Reznik VM, et al. Treatment of childhood prednisone-resistant nephrotic syndrome and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis with intravenous methylprednisolone and oral alkylating agents. Nephron 46:73–77. 1987;


34. Mendoza SA, Reznik VM, Griswold WR, Krensky AM, Yorgin PD, Tune BM. Treatment of steroid-resistant focal segmental glomerulosclerosis with pulse methylprednisolone and alkylating agents. Pediatr Nephrol 4:303–307. 1990;


35. Tune BM, Kirpekar R, Sibley RK, Reznik VM, Griswold WR, Mendoza SA. Intravenous methylprednisolone and oral alkylating agent therapy of prednisone-resistant pediatric focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: a long-term follow-up. Clin Nephrol 43:84–88. 1995;

36. Tune BM, Lieberman E, Mendoza SA. Steroid-resistant nephrotic focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: a treatable disease. Pediatr Nephrol 10:772–778. 1996;


37. Sakemi T, Fujimoto S, Fujimi S, Yamamoto Y, Etoh T, Yamaguchi M. Difference between renal failure associated with methylprednisolone pulse therapy and deterioration of renal function unrelated to methylprednisolone therapy. Am J Nephrol 13:132–137. 1993;





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print
















