| Kidney Res Clin Pract > Volume 39(2); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
Acknowledgments
Notes
Funding
This study was supported by the Research Program funded by the Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention (2011E3300300, 2012E3301100, 2013E3301600, 2013E3301601, 2013E3301602, 2016E3300200, and 2019E320100).
AuthorsŌĆÖ contributions
All of the authors contributed to the formation of the overall concept of the study. Minjung Kang, Eunjeong Kang, and Hyunjin Ryu drafted the manuscript. Kook-Hwan Oh revised and edited the manuscript. Kook-Hwan Oh, Seung Hyeok Han, Tae-Hyun Yoo, Soo Wan Kim, Sue K. Park, Kyu-Beck Lee, Dong-Wan Chae, Yeong Hoon Kim, and Curie Ahn designed the main concept of the study. Curie Ahn and Kook-Hwan Oh funded the study.
Figure┬Ā1
Incidences of major outcomes of KoreaN Cohort Study for Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease (KNOW-CKD) and comparison with the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) cohort.

Figure┬Ā2
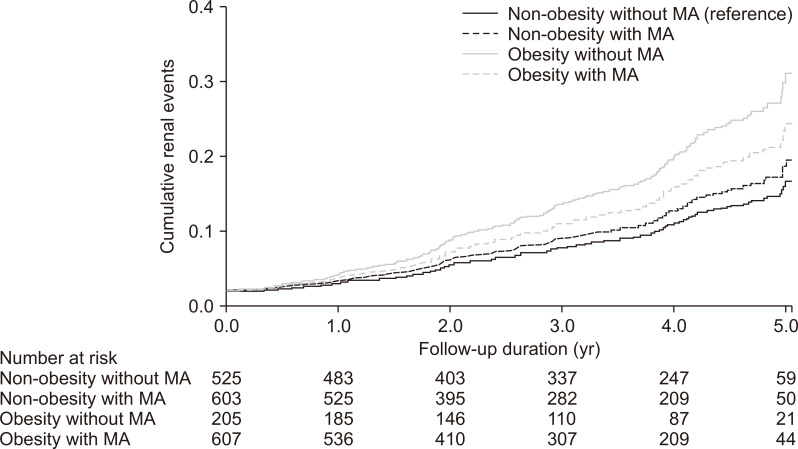
Adjusted Kaplan-Meier curve for cumulative renal events according to metabolic subtypes [40], reproduced with permission.
Figure┬Ā3
Association of measured 24-hour urinary sodium excretion with hazard ratio of chronic kidney disease progression in fully-adjusted model [41].

Figure┬Ā4
The association between high-sensitivity troponin T (hs-TnT) and longitudinal echocardiographic changes [61].

Figure┬Ā5
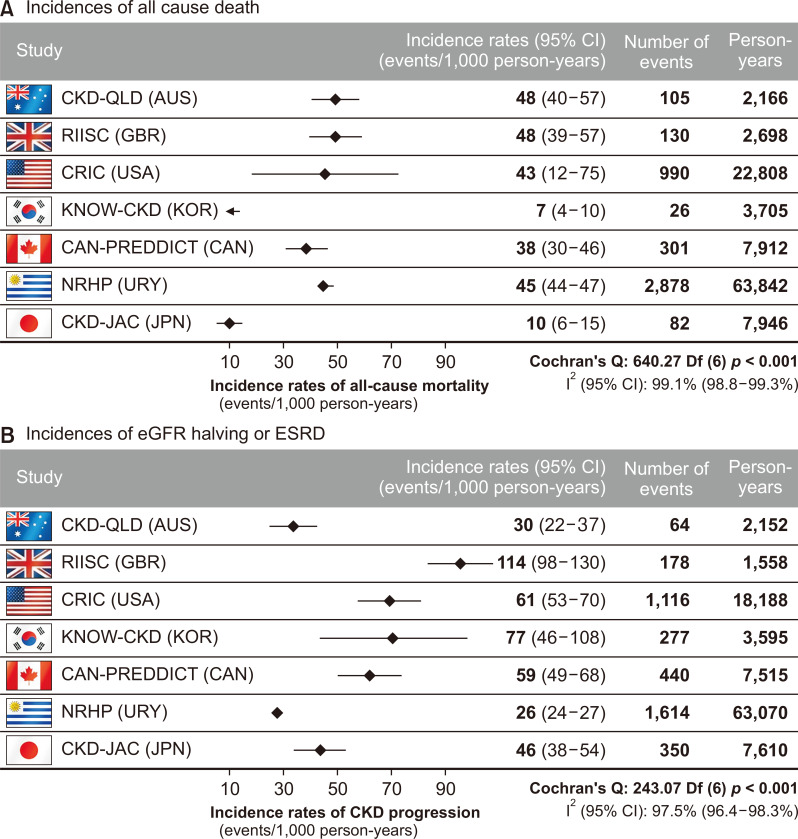
Adjusted incidence rates of all-cause death (A) and composite of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) halving or end-stage renal disease (ESRD) (B) across the International Network of Chronic Kidney Disease studies (iNET-CKD) [51], reproduced with permission.
Table┬Ā1
| Parameter | Screen | At entry | 6 mo | 1 yr | 2 yr | 3 yr | 4 yr | 5 yr | 6 yr | 7 yr | 8 yr | 9 yr | 10 yr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Informed consent | ŌŚÅ | ||||||||||||
| Demographic information, Medical History | ŌŚÅ | ||||||||||||
| Recent events | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ||
| Medications | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | |
| HRQOL/Health related questionnaire | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | |||||||||||
| BP/anthropometry | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | |
| CBC, chemistry, Cra, eGFR, Cystatin Ca, HbA1c | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | |
| Lipid panel, CRP, iron panel | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ||||||||||
| Intact PTHa, 25 Da, 1,25 Da, troponin Ta | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ||||||||||
| UA with microscopy | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ||||||||||
| 24HU ŌĆō Na/K/Ca/P/Cr/Urea/Uric acid/protein, Spot urine electrolytesa, albumina, proteina, osmolalitya, Cra | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ||||||||||
| ECG, chest X ray | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | |||||||||
| EchoCG, PWV, ABI, Coronary CT, LS spine lateral X-ray, DEXA BMD | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | |||||||||||
| Biosamples for DNA | ŌŚÅ | ||||||||||||
| Serum/urine biosample | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | |||||
| Fundus exam (DM subgroup) | ŌŚÅ | ||||||||||||
| Abdomen CT (PKD subgroup) | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | ŌŚÅ | |||||||
| Family screen (PKD subgroup) | ŌŚÅ | ||||||||||||
1,25 D, 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D; 24HU, 24-hour urine; 25 D, 25-hydroxyvitamine D; ABI, ankle-brachial index; BP, blood pressure; CBC, complete blood count; Cr, creatinine; CRP, C-reactive protein; CT, computed tomography; DEXA BMD, dual energy x-ray absorptiometry bone mineral density; DM, diabetes mellitus; ECG, electrocardiogram; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; HRQOL, health-related quality of life; KNOW-CKD, KoreaN Cohort Study for Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease; LS, lumbosacral; PKD, polycystic kidney disease; PTH, parathyroid hormone; PWV, pulse wave velocity; UA, urinalysis.
Table┬Ā2
| Cause of CKD | Total (n = 2,238) | GN (n = 810) | DN (n = 519) | HTN (n = 409) | PKD (n = 364) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 53.7 ┬▒ 12.2 | 49.8 ┬▒ 12.1 | 59.3 ┬▒ 9.4 | 59.6 ┬▒ 10.8 | 47 ┬▒ 10.6 | < 0.001* |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male | 1,369 (61.2) | 451 (55.7) | 357 (68.8) | 295 (72.1) | 184 (50.5) | < 0.001ŌĆĀ |
| Female | 869 (38.8) | 359 (44.3) | 162 (31.2) | 114 (27.9) | 180 (49.5) | |
| Educational attainment | ||||||
| Illiteracy | 15 (0.8) | 6 (0.9) | 1 (0.2) | 5 (1.4) | 2 (0.6) | < 0.001ŌĆĀ |
| Graduated elementary school | 239 (10.8) | 56 (8.0) | 71 (16.0) | 53 (14.7) | 19 (5.6) | |
| Graduated middle school | 259 (11.7) | 62 (8.9) | 76 (17.2) | 41 (11.4) | 24 (7.0) | |
| Graduated high school | 785 (35.3) | 268 (38.3) | 145 (32.7) | 110 (30.6) | 98 (28.7) | |
| Graduated college or more | 906 (40.8) | 308 (43.9) | 150 (33.8) | 151 (42.0) | 198 (58.1) | |
| Smoking | ||||||
| Never smoker | 1,202 (53.9) | 478 (59.1) | 240 (46.8) | 183 (44.9) | 228 (62.6) | < 0.001ŌĆĀ |
| Current smoker | 349 (15.7) | 115 (14.2) | 84 (16.4) | 71 (17.4) | 55 (15.1) | |
| Former smoker | 677 (30.4) | 216 (26.7) | 189 (36.8) | 154 (37.7) | 81 (22.3) | |
| Comorbid disease | ||||||
| Coronary artery disease | 118 (5.3) | 14 (1.7) | 60 (11.6) | 32 (7.8) | 2 (0.5) | < 0.001ŌĆĀ |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 78 (3.5) | 13 (1.6) | 32 (6.2) | 20 (4.9) | 1 (0.3) | < 0.001ŌĆĀ |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 135 (6.0) | 19 (2.3) | 51 (9.8) | 38 (9.3) | 21 (5.8) | < 0.001ŌĆĀ |
| Diabetes | 755 (33.7) | 70 (8.6) | 519 (100.0) | 72 (17.6) | 12 (3.3) | < 0.001ŌĆĀ |
| Hypertension | 2,150 (96.1) | 785 (96.9) | 513 (98.8) | 407 (99.5) | 314 (86.3) | < 0.001ŌĆĀ |
| Congestive heart failure | 34 (1.5) | 7 (0.9) | 12 (2.3) | 10 (2.4) | 2 (0.5) | 0.025ŌĆĪ |
| Arrhythmia | 56 (2.5) | 18 (2.2) | 16 (3.1) | 18 (4.4) | 2 (0.5) | 0.006ŌĆĀ |
| Age-adjusted modified CCI | ||||||
| Low (Ōēż 3) | 1,174 (52.5) | 627 (77.4) | 24 (4.6) | 153 (37.4) | 317 (87.1) | < 0.001ŌĆĀ |
| Moderate (4-5) | 652 (29.1) | 155 (19.1) | 204 (39.3) | 193 (47.2) | 45 (12.4) | |
| High (6-7) | 347 (15.5) | 25 (3.1) | 242 (46.6) | 56 (13.7) | 2 (0.5) | |
| Very high (8-9) | 65 (2.9) | 3 (0.4) | 49 (9.4) | 7 (1.7) | 0 (0.0) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.6 ┬▒ 3.4 | 24.2 ┬▒ 3.3 | 25.2 ┬▒ 3.2 | 25.1 ┬▒ 3.5 | 23.5 ┬▒ 3 | < 0.001* |
| BP variables | ||||||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 127.8 ┬▒ 16.2 | 123.4 ┬▒ 14.2 | 134.3 ┬▒ 18.5 | 127.8 ┬▒ 15.9 | 128.3 ┬▒ 13.3 | < 0.001* |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 77 ┬▒ 11.1 | 75.6 ┬▒ 10.1 | 75.7 ┬▒ 11.7 | 77.7 ┬▒ 11.5 | 81 ┬▒ 10.4 | < 0.001* |
| Pulse pressure (mmHg) | 50.8 ┬▒ 12.2 | 47.8 ┬▒ 10.6 | 58.5 ┬▒ 13.4 | 50.1 ┬▒ 11.3 | 47.3 ┬▒ 9.8 | < 0.001* |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 53.1 ┬▒ 30.7 | 60.1 ┬▒ 31.4 | 36.6 ┬▒ 21.9 | 42.3 ┬▒ 21.7 | 72.9 ┬▒ 32.9 | < 0.001* |
| Urine protein/24 hr (mg/day) | 1,353 ┬▒ 2,139 | 1,292 ┬▒ 1,524 | 2,664 ┬▒ 3,168 | 766 ┬▒ 1,133 | 178 ┬▒ 256 | < 0.001* |
| ACEI or ARB therapy | 1,907 (85.4) | 726 (89.7) | 448 (86.8) | 333 (81.6) | 285 (78.3) | < 0.001ŌĆĀ |
| CKD stage | ||||||
| Stage G1 | 265 (11.8) | 131 (16.2) | 13 (2.5) | 11 (2.7) | 94 (25.8) | < 0.001ŌĆĀ |
| Stage G2 | 419 (18.7) | 180 (22.2) | 44 (8.5) | 48 (11.7) | 118 (32.4) | |
| Stage G3a | 403 (18.0) | 163 (20.1) | 72 (13.9) | 95 (23.2) | 52 (14.3) | |
| Stage G3b | 484 (21.6) | 158 (19.5) | 131 (25.2) | 112 (27.4) | 45 (12.4) | |
| Stage G4 | 522 (23.3) | 138 (17.0) | 198 (38.2) | 118 (28.9) | 42 (11.5) | |
| Stage G5 (predialysis) | 145 (6.5) | 40 (4.9) | 61 (11.8) | 25 (6.1) | 13 (3.6) | |
ACEI, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; BMI, body mass index; BP, blood pressure; CCI, Charlson comorbidity index; CKD, chronic kidney disease; DN, diabetic nephropathy; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; G, grade; GN, glomerulonephritis; HTN, hypertensive nephropathy; KNOW-CKD, KoreaN Cohort Study for Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease; PKD, polycystic kidney disease.
Table┬Ā3
Table┬Ā4
Table┬Ā5
| Time frame | Biomarker | Outcome | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | Adiponectin | MS | Hypoadiponectinemia is independently associated with the metabolic syndrome in CKD [53]. |
| C | Adiponectin | PEW | High serum adiponectin is independently associated with PEW. Among PEW indicators, serum adiponectin is closely associated with urine creatinine excretion as an indirect measure of muscle mass [54]. |
| C | Adiponectin | Albuminuria and renal function | Serum adiponectin is higher in patients with increasing albuminuria, and these levels are associated with albuminuria, renal insufficiency and lipid profiles [55]. |
| C | Adiponectin | hfPWV | The independent and significant correlation of serum adiponectin concentration with hfPWV in CKD implicates adiponectin in CKD-associated aortic stiffness [56]. |
| C, L | Adiponectin | Anemia | A high serum adiponectin level is independently associated with a low hemoglobin level and predicts the development of anemia in patients with CKD [57]. |
| L | Adiponectin | Renal event | Serum adiponectin may be a biomarker of renal dysfunction rather than a true risk factor in CKD progression [58]. |
| C | FGF23 | CAC | High serum FGF23 was associated with CAC in CKD patients with high adiponectin, but not in those with low adiponectin [59]. |
| L | HDL cholesterol | Renal event | A U-shaped association was observed between serum HDL-C levels and adverse renal outcomes [60]. |
| C, L | hs-TnT | LV structure and function, new LVH | hs-TnT is strongly associated with alterations of LV structure and diastolic dysfunction for both eGFR strata. Baseline hs-TnT levels are predictive of new LVH on follow-up [61]. |
| C | Klotho | LV mass index | Serum Klotho is an independent biomarker of left ventricular mass index [28]. |
| C | Klotho | MS | MS is prevalent in CKD. Serum Klotho is inversely associated with the presence of MS in patients with CKD [62]. |
| C | OPG | baPWV | Non-traditional, kidney-related cardiovascular risk factors in addition to traditional cardiovascular risk factors are related to serum level of OPG in CKD. Serum OPG level is significantly related to baPWV [63]. |
| C | Urine creatinine excretion | PWV | 24-hour urine creatinine is a marker of muscle mass. Low creatinine excretion is associated with high PWV, suggesting a relationship between decreased muscle mass and arterial stiffness [64]. |
| L | Urine Na/K ratio | Renal event | The Na/K ratio in urine is an index of dietary sodium and potassium intake. The higher Na/K ratio in 24-hour urine collection is associated with higher rate of CKD progression [65]. |
| C, L | Urine AGT | Urinary K excretion, renal event | High urinary AGT level is associated with increased urinary K excretion and renal outcome in patients with PKD [66]. |
AGT, angiotensinogen; baPWV, brachial-to-ankle pulse wave velocity; C, cross-sectional; CAC, coronary artery calcification; CKD, chronic kidney disease; FGF23, fibroblast growth factor 23; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; hfPWV, heart-to-femoral pulse wave velocity; hs-TnT, high sensitivity troponin T; KNOW-CKD, KoreaN Cohort Study for Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease; L, longitudinal; LV, left ventricle; LVH, left ventricular hypertrophy; MS, metabolic syndrome; OPG, osteoprotegerin; PEW, protein-energy wasting; PKD, polycystic kidney disease.
Table┬Ā6
| Characteristics | Phase I | Phase II |
|---|---|---|
| Timing of enrollment (year) | 2011-2016 | 2019-2021 |
| Number of participating lefts | 9 | 13 |
| Number enrolled | 2,238 | 1,500a |
| Age (yr) | 20-75 | 45-79 |
| CKD Stage or eGFR |
CKD G1-G5 (pre-dialysis) |
20-60 mL/min/1.73 m2 |
| Diabetes | 34% | 50%a |




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Supplement 1
Supplement 1 Print
Print
















