-
Editorial
February 19, 2024
- On operational definitions of mortality
- Hakmook Kang
- Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024;43(2):131-132.
- Editorial
- On operational definitions of mortality
- Hakmook Kang
- Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024;43(2):131-132. Published online February 19, 2024
-
- Review Articles
- Which blood pressure metrics should be used in patients on dialysis?
- Ji Yong Jung
- Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024;43(2):133-142. Published online November 14, 2023
-
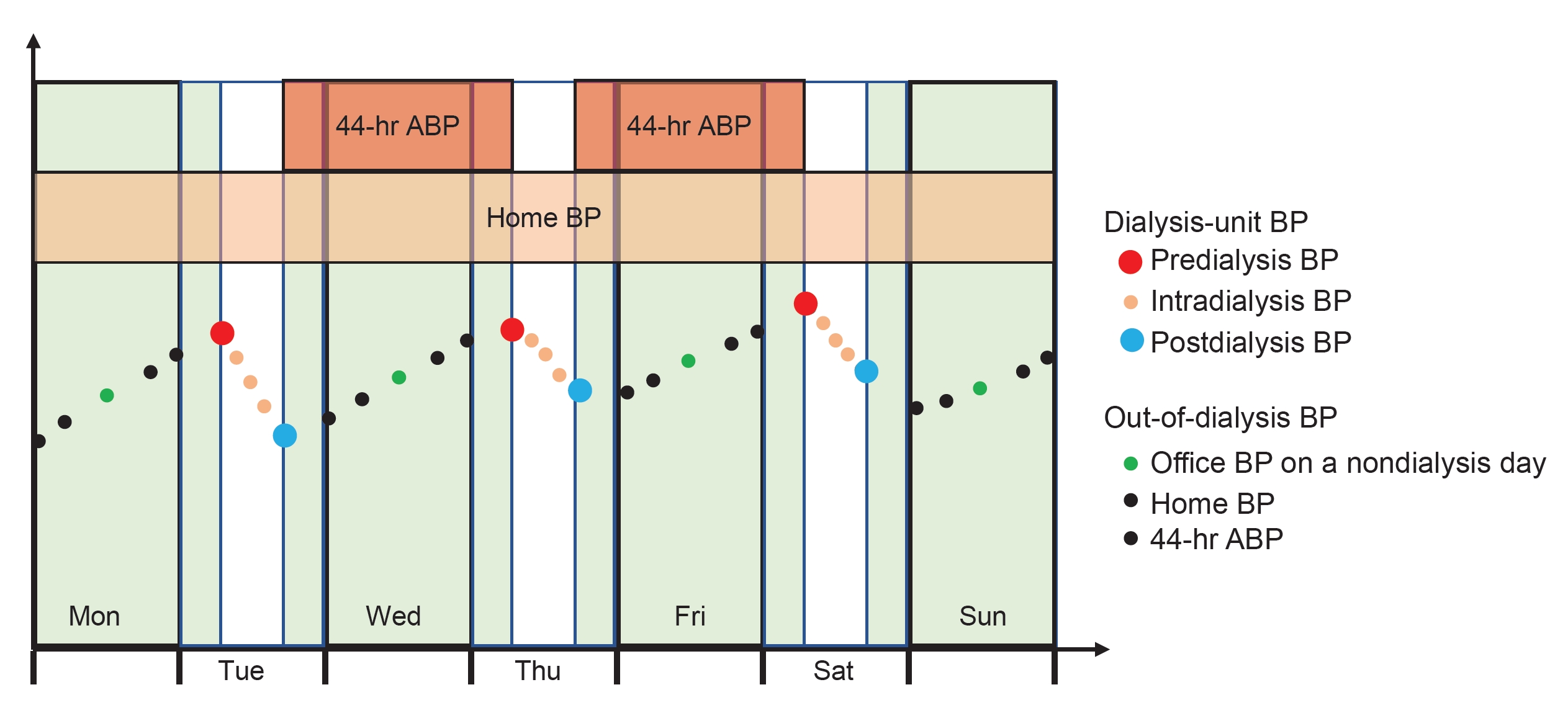
Remarkable progress has recently been achieved in blood pressure (BP) control based on key research findings in the general population. It has been observed that maintaining BP slightly lower than previously recommended goals leads to better clinical outcomes, provided that patients can tolerate it. Previously, BP control targets for dialysis patients were extrapolated from studies conducted on the general population....
- Pharmacologic therapeutics in sarcopenia with chronic kidney disease
- Ran-hui Cha
- Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024;43(2):143-155. Published online February 19, 2024
-
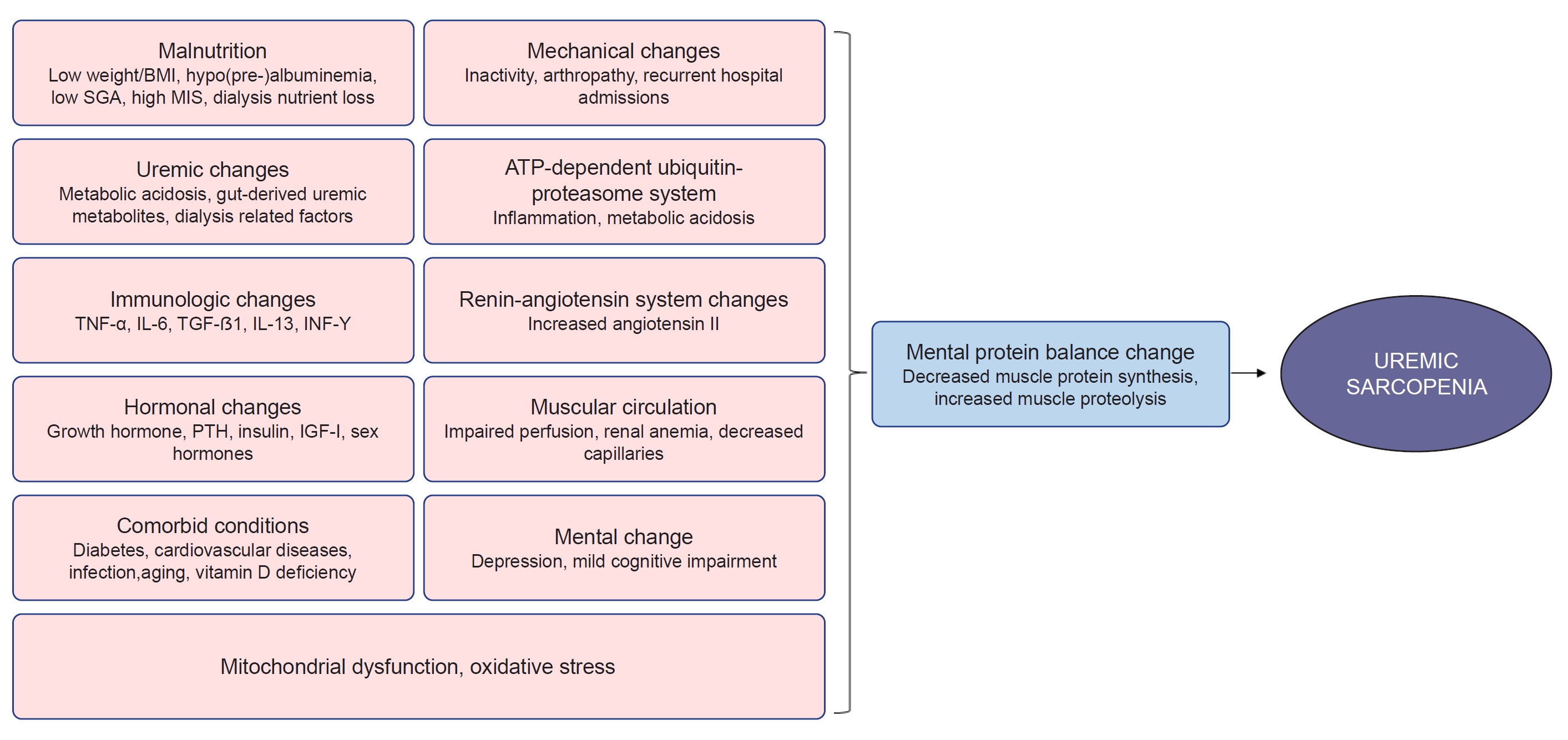
Inflammation, metabolic acidosis, renin-angiotensin system activation, insulin resistance, and impaired perfusion to skeletal muscles, among others, are possible causes of uremic sarcopenia. These conditions induce the activation of the nuclear factor-kappa B and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways, adenosine triphosphate ubiquitin-proteasome system, and reactive oxygen species system, resulting in protein catabolism. Strategies for the prevention and treatment of sarcopenia in chronic...
- Original Articles
- Validation of operational definitions of mortality in a nationwide hemodialysis population using the Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service databases of Korea
- Dong Hee Lee, Ye-Jee Kim, Hyangkyoung Kim, Hyung Seok Lee
- Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024;43(2):156-164. Published online February 23, 2023
-
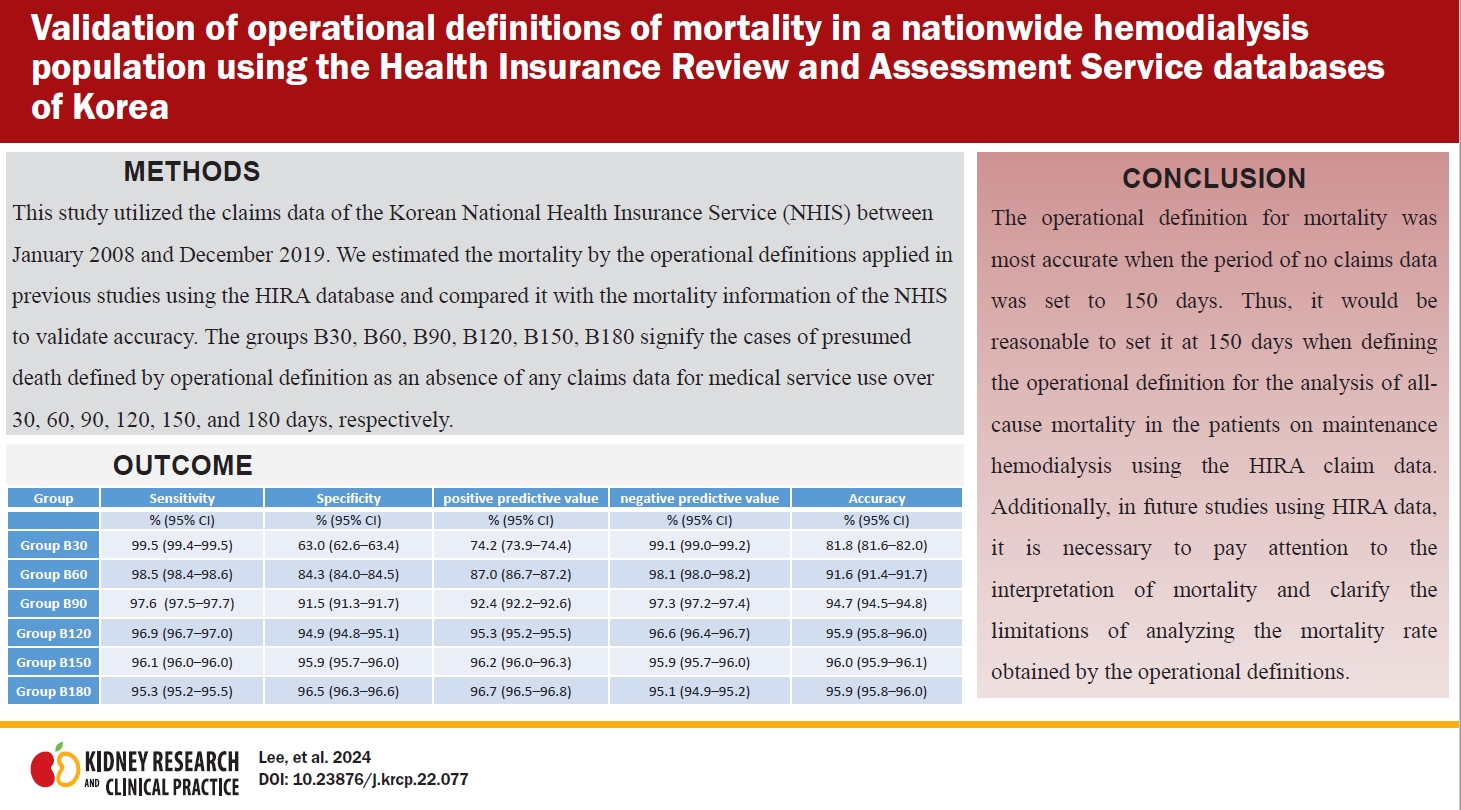
Background: Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service’s (HIRA) claims data have been used in studies of hemodialysis patients even though information about mortality is not provided in this database. Mortality analysis using HIRA data has been conducted using various operational definitions that have not been validated. This study aimed to validate operational definitions of mortality for maintenance hemodialysis patients that...
- Glomerulonephritis following COVID-19 infection or vaccination: a multicenter study in South Korea
- Hyung Woo Kim, Eun Hwa Kim, Yun Ho Roh, Young Su Joo, Minseob Eom, Han Seong Kim, Mi Seon Kang, HoeIn Jeong, Beom Jin Lim, Seung Hyeok Han, Minsun Jung
- Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024;43(2):165-176. Published online March 20, 2024
-
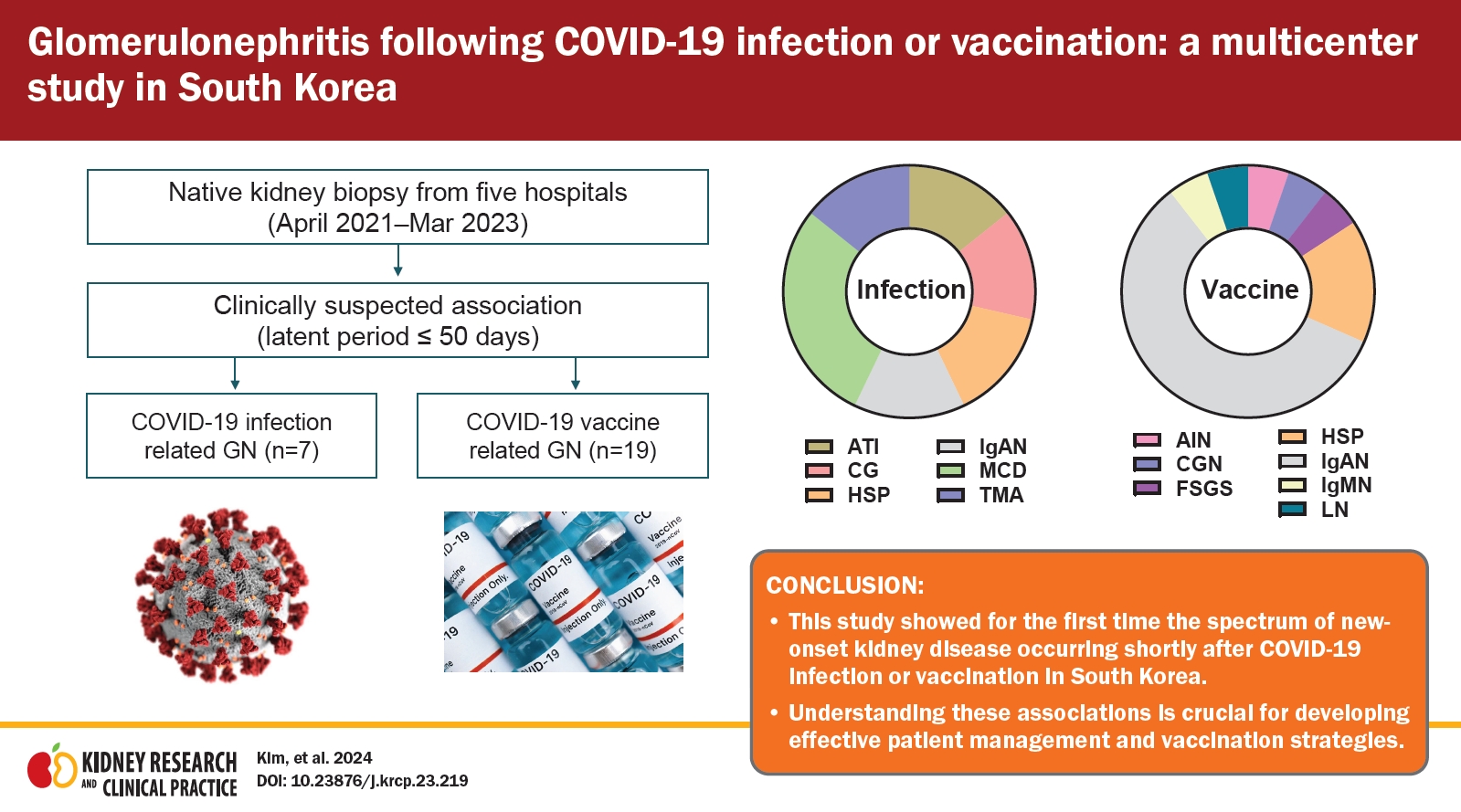
Background: Despite the widespread impact of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (coronavirus disease 2019, COVID-19) and vaccination in South Korea, our understanding of kidney diseases following these events remains limited. We aimed to address this gap by investigating the characteristics of glomerular diseases following the COVID-19 infection and vaccination in South Korea. Methods: Data from multiple centers were...
- Vitamin D and narrowband ultraviolet B phototherapy for chronic kidney disease-associated pruritus
- Youn Kyung Kee, Hee Jung Jeon, Jieun Oh, Dong Ho Shin
- Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024;43(2):177-185. Published online March 22, 2023
-
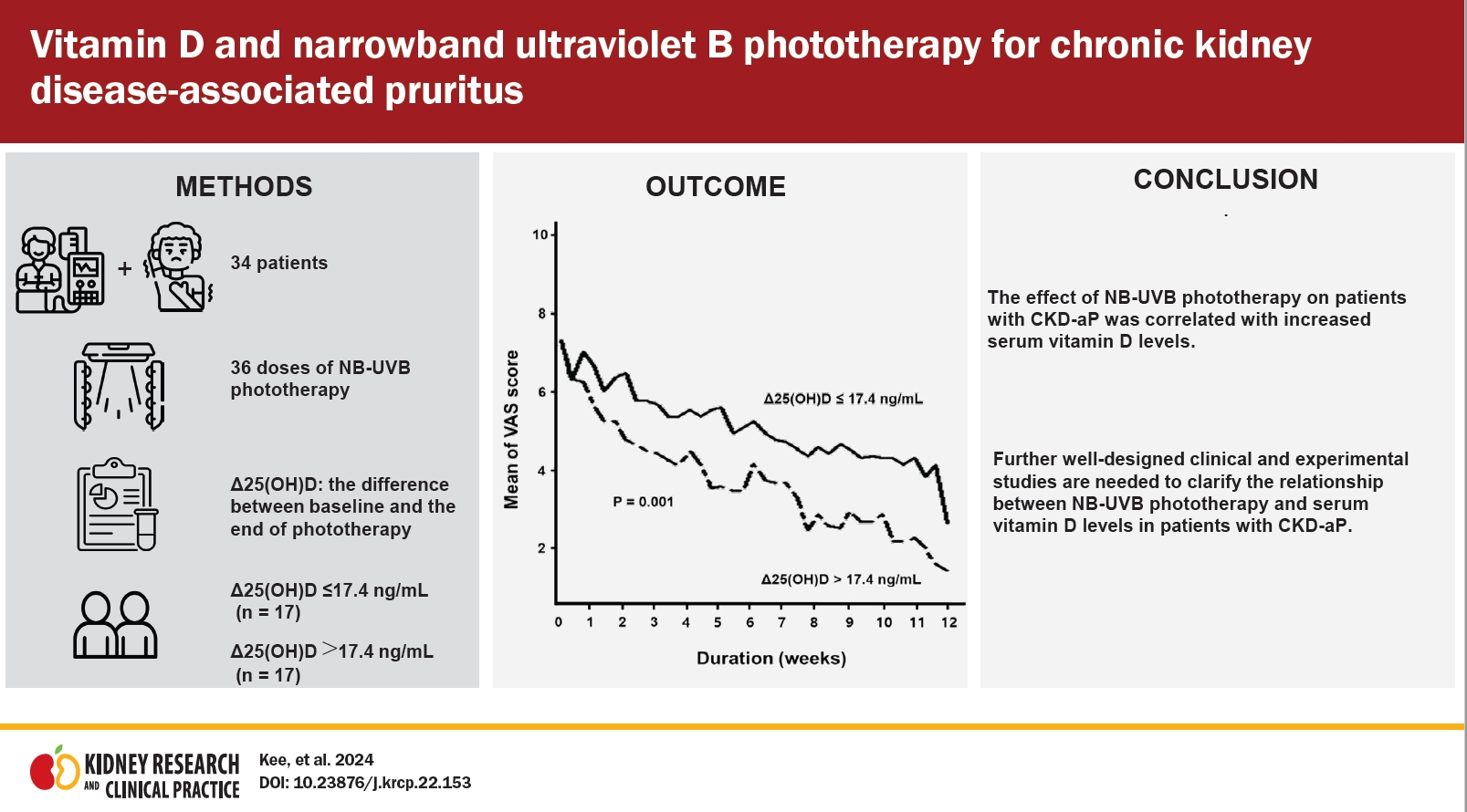
Background: In addition to improving the serum vitamin D balance, narrowband ultraviolet B (NB-UVB) phototherapy can effectively treat chronic kidney disease-associated pruritus (CKD-aP). We investigated the degree of CKD-aP amelioration according to changes in the serum vitamin D level after NB-UVB phototherapy. Methods: This was a before–after clinical study in patients with refractory CKD-aP on hemodialysis. NB-UVB phototherapy was administered... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.23876/j.krcp.22.153 [Epub ahead of print]
- Role of APE1/Ref-1 in hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in human renal HK-2 cells
- Ha Yeon Kim, Jung Sun Park, Byeong Hwa Jeon, Hong Sang Choi, Chang Seong Kim, Seong Kwon Ma, Soo Wan Kim, Eun Hui Bae
- Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024;43(2):186-201. Published online May 23, 2023
-

Background: Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1/redox factor-1 (APE1/Ref-1) is a multipotent protein that plays essential roles in cellular responses to oxidative stress. Methods: To examine the role of APE1/Ref-1 in ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injuries and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced renal tubular apoptosis, we studied male C57BL6 mice and human proximal tubular epithelial (HK-2) cells treated with H2O2 at different concentrations. The colocalization of APE1/Ref-1...
- Risk of mortality and cause of death according to kidney function parameters: a nationwide observational study in Korea
- Sehyun Jung, Soojin Lee, Yaerim Kim, Semin Cho, Hyuk Huh, Yong Chul Kim, Seung Seok Han, Hajeong Lee, Jung Pyo Lee, Kwon Wook Joo, Chun Soo Lim, Yon Su Kim, Dong Ki Kim, Kyungdo Han, Sehoon Park
- Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024;43(2):202-215. Published online March 20, 2024
-
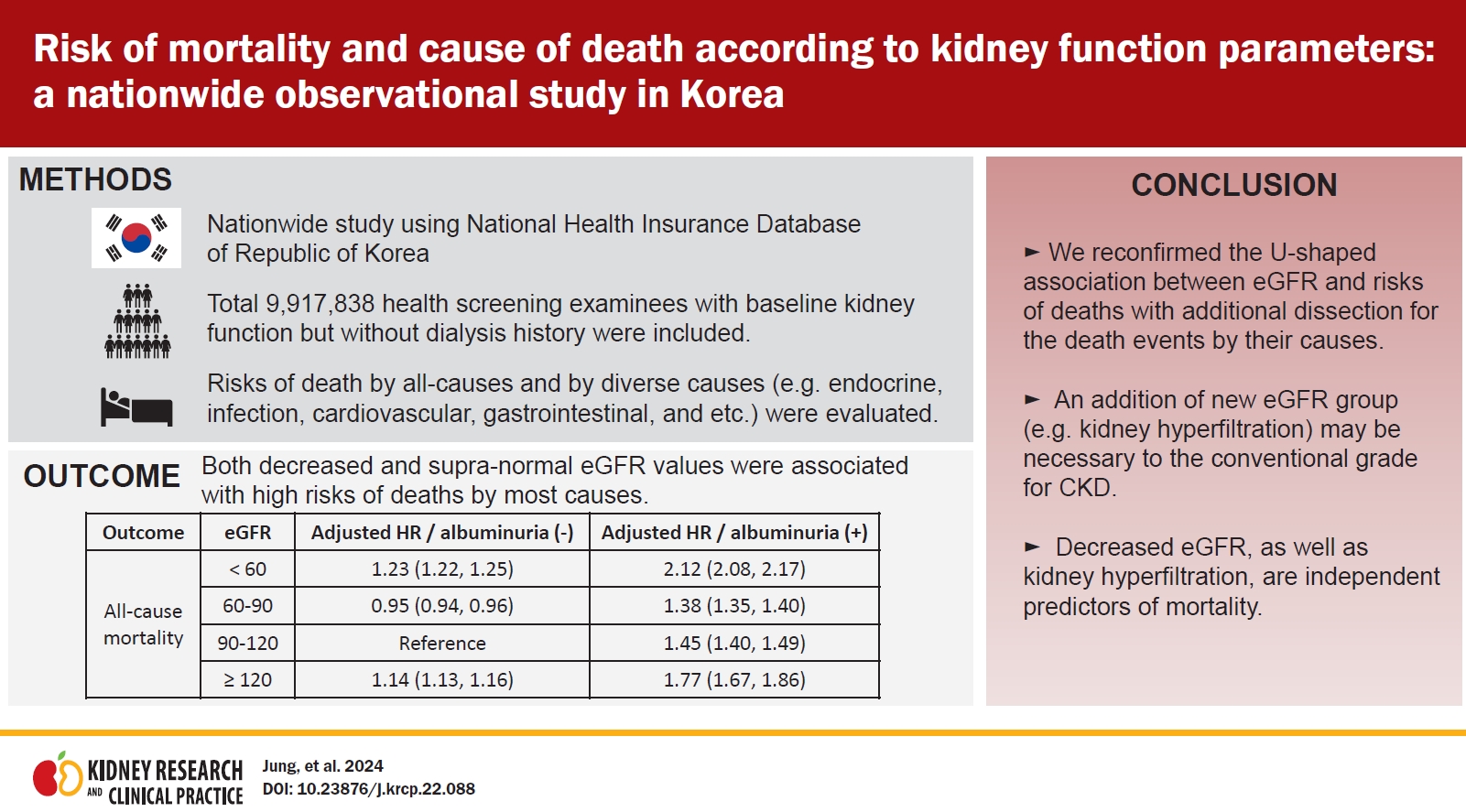
Background: Further study is warranted to determine the association between estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) or albuminuria and the risk of death from diverse causes. Methods: We screened >10 million general health screening examinees who received health examinations conducted in 2009 using the claims database of Korea. After the exclusion of those previously diagnosed with renal failure and those with...
- A collaborative model between dialysis clinics and a hospital center improves the quality of vascular access care and intervention for hemodialysis patients
- Chung-Kuan Wu, Yu-Wei Fang, Chia-Hsun Lin
- Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024;43(2):216-225. Published online May 11, 2023
-
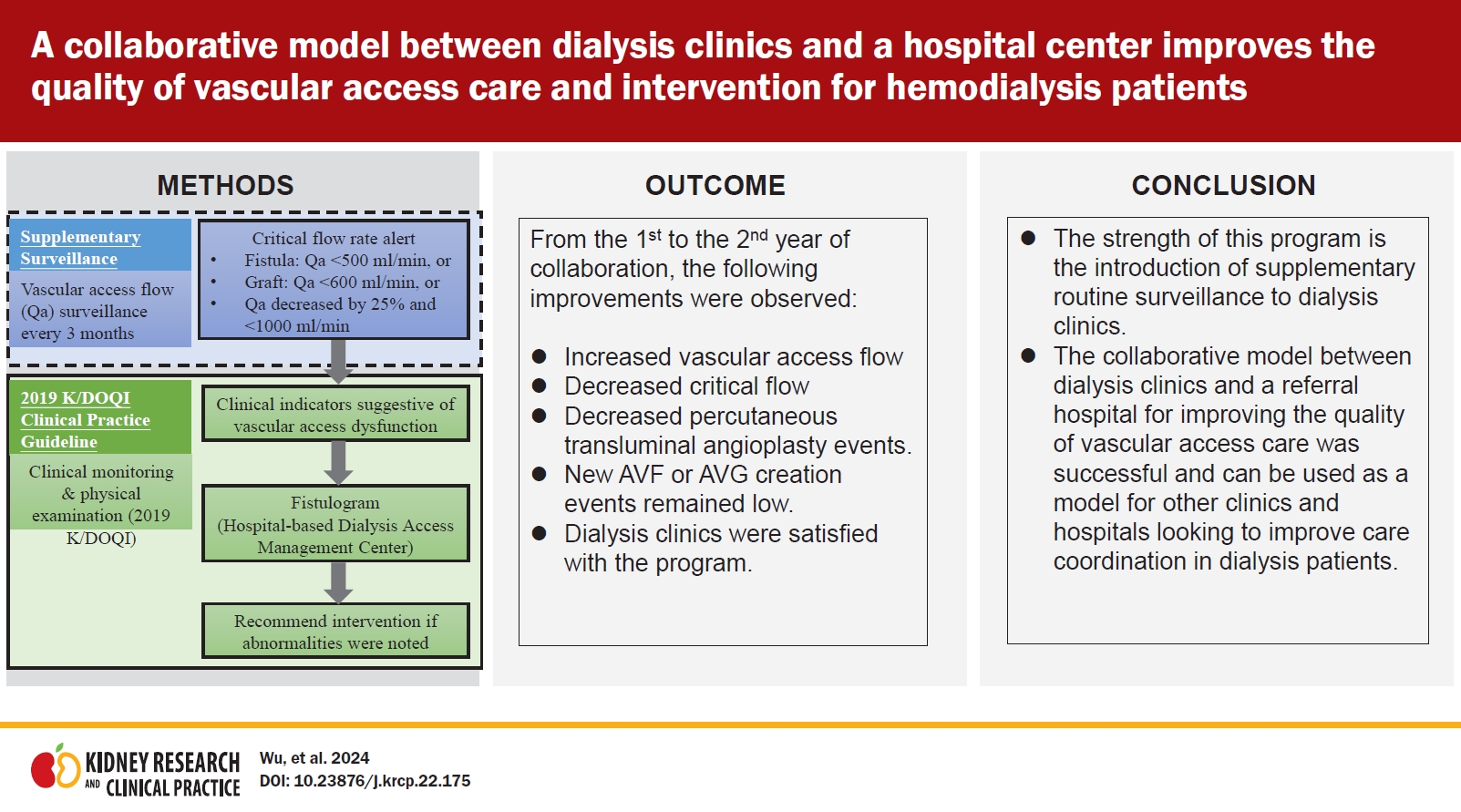
Background: This study reports the outcomes of a collaborative program between dialysis clinics and a referral hospital, which consisted of clinical monitoring and supplementary routine surveillance, for improving the quality of vascular access care. Methods: This retrospective observational study was performed at five dialysis clinics as part of a 2-year collaborative program (2019–2020) in conjunction with a hospital-based dialysis access...
- Circulatory endostatin level and risk of cardiovascular events in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis
- Jin Sug Kim, Miji Kim, Kyung Hwan Jeong, Ju-Young Moon, Sang Ho Lee, Gang Jee Ko, Dong-Young Lee, So Young Lee, Yang Gyun Kim, Hyeon Seok Hwang
- Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024;43(2):226-235. Published online March 13, 2024
-
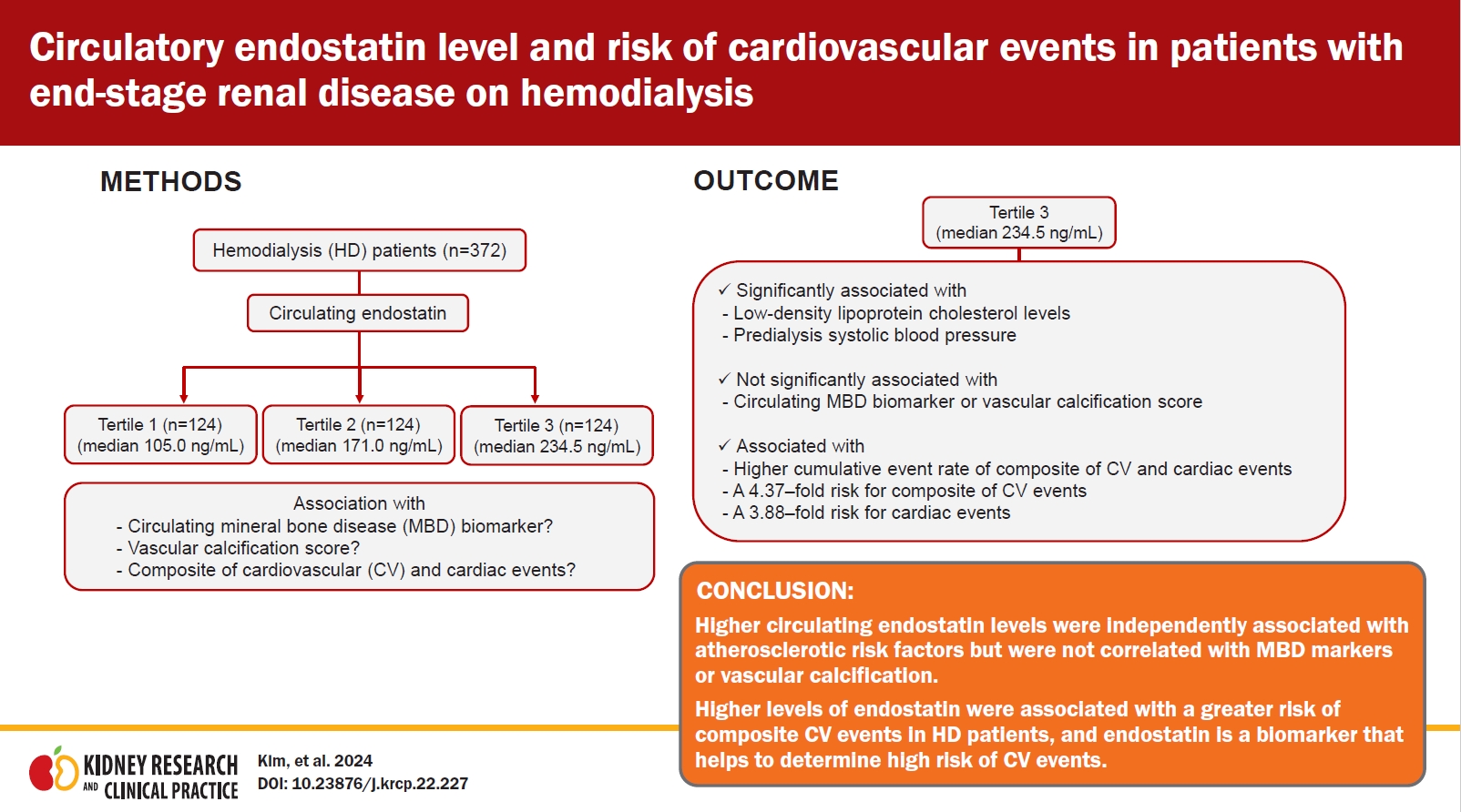
Background: Endostatin is released during extracellular matrix remodeling and is involved in the development of vascular pathology and cardiovascular (CV) disease. However, the role of circulating endostatin as a biomarker of vascular calcification and CV events in patients undergoing hemodialysis (HD) remains unclear. Methods: A total of 372 patients undergoing HD were prospectively recruited. Plasma endostatin levels were measured at...
- Prediction of diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation using patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells
- Sun Woo Lim, Yoo Jin Shin, Sheng Cui, Eun Jeong Ko, Byung Ha Chung, Chul Woo Yang
- Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024;43(2):236-249. Published online June 15, 2023
-
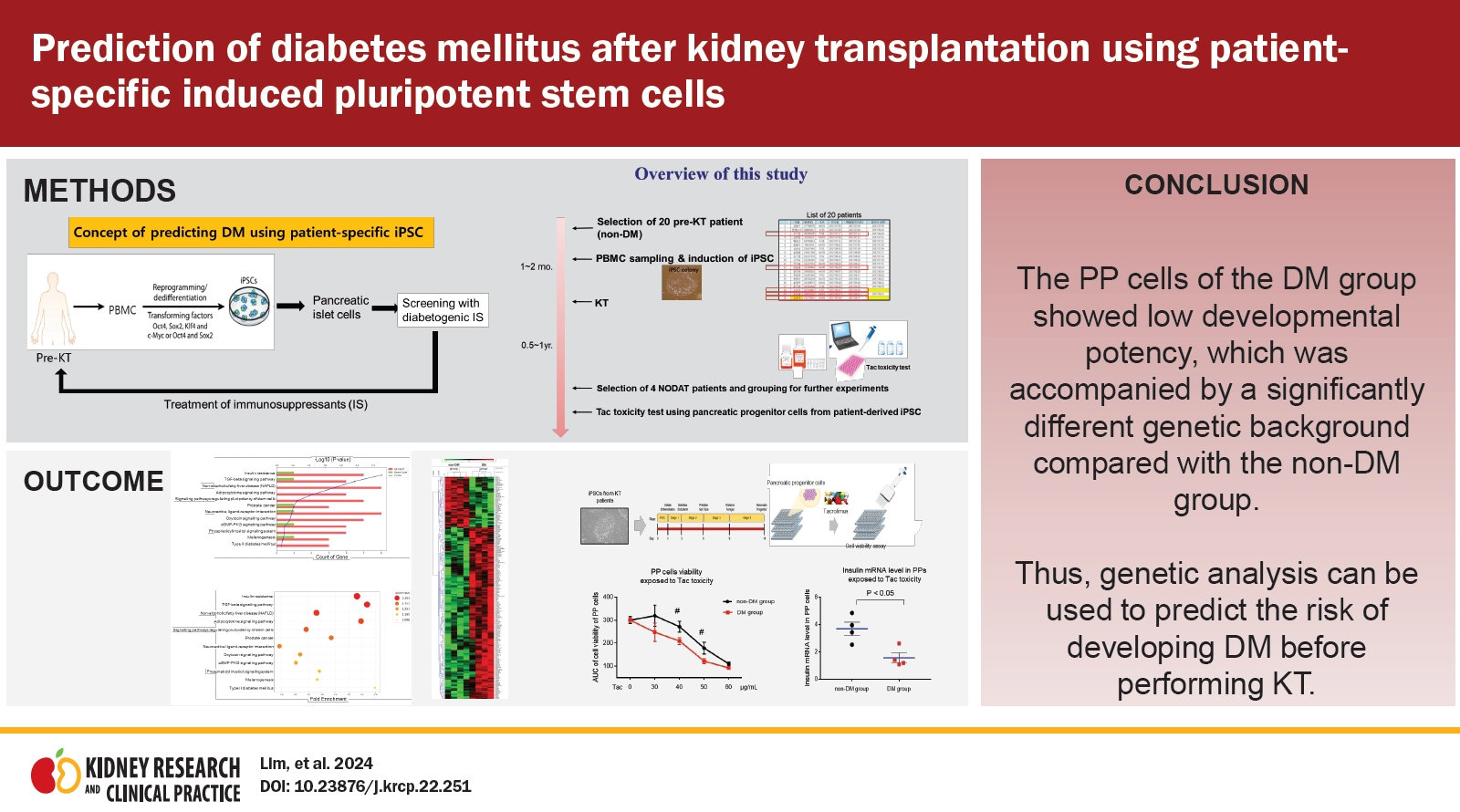
Background: Multiple risk factors are involved in new-onset diabetes mellitus (DM) after organ transplantation; however, their ability to predict clinical prognosis remains unclear. Therefore, we investigated whether patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) could help predict DM development before performing kidney transplantation (KT). Methods: We first performed whole transcriptome and functional enrichment analyses of KT patient-derived iPSCs. Our results revealed...
- Images in Practice
- Renal infarction caused by spontaneous renal artery dissection after playing golf
- Seung Hee Jeong, Dong Min Kang, Ju Hwan Oh, A Young Cho, In O Sun, Kwang Young Lee, Haeun Lee
- Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024;43(2):250-252. Published online March 18, 2024
-
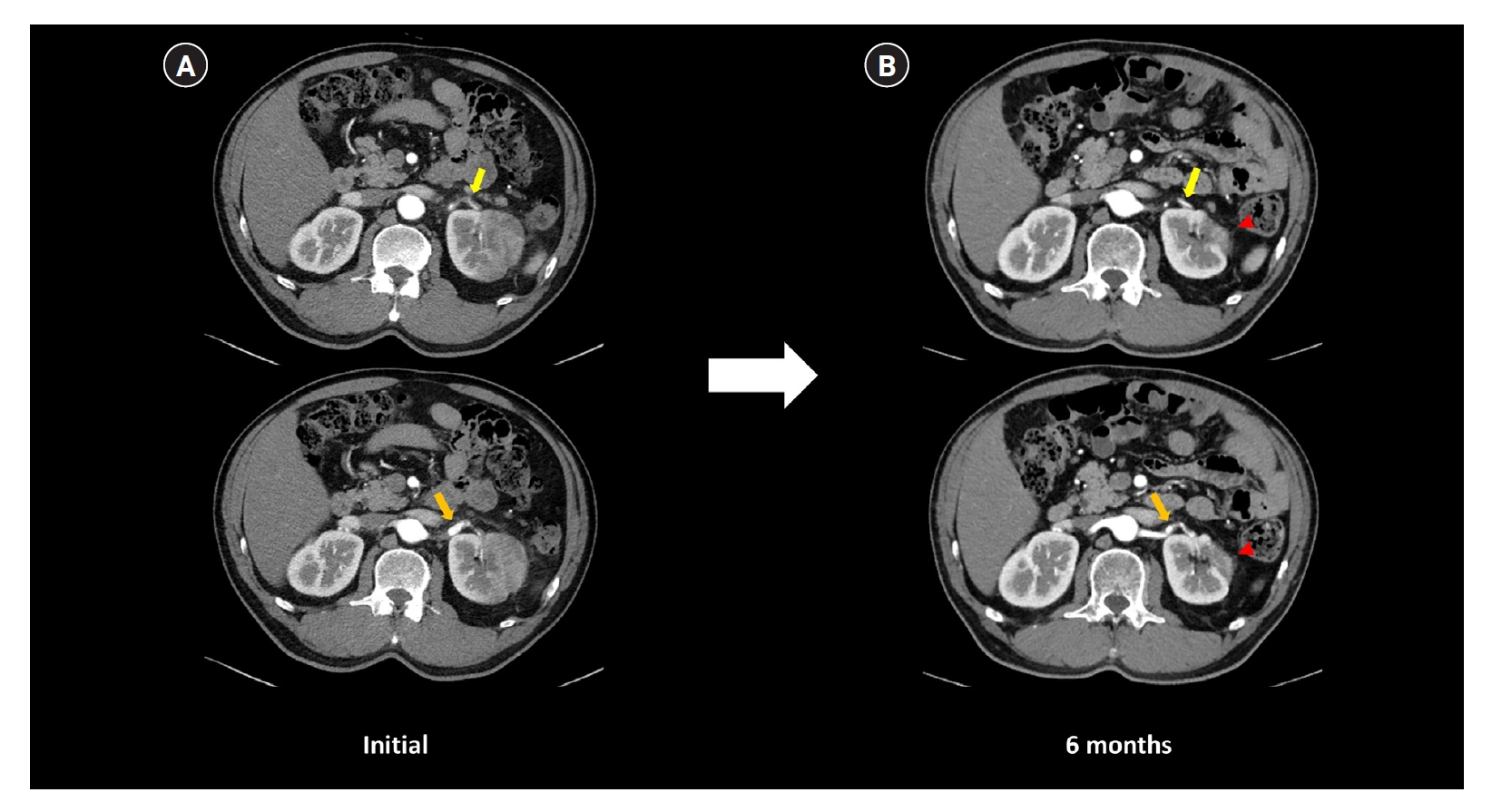
- Correspondence
- Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis in the elderly: a case of cryoglobulinemic glomerulopathy not to be overlooked
- Hyeran Park, Seyoung Ryou, Seung Yun Chae, Eun Ah Kim, Jong-Mi Lee, Yaeni Kim, Yeong-Jin Choi, Cheol Whee Park
- Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2024;43(2):253-256. Published online March 27, 2024
-