| Kidney Res Clin Pract > Volume 41(6); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
Figure 1.
Frailty, CKD, and dementia in the aging population.
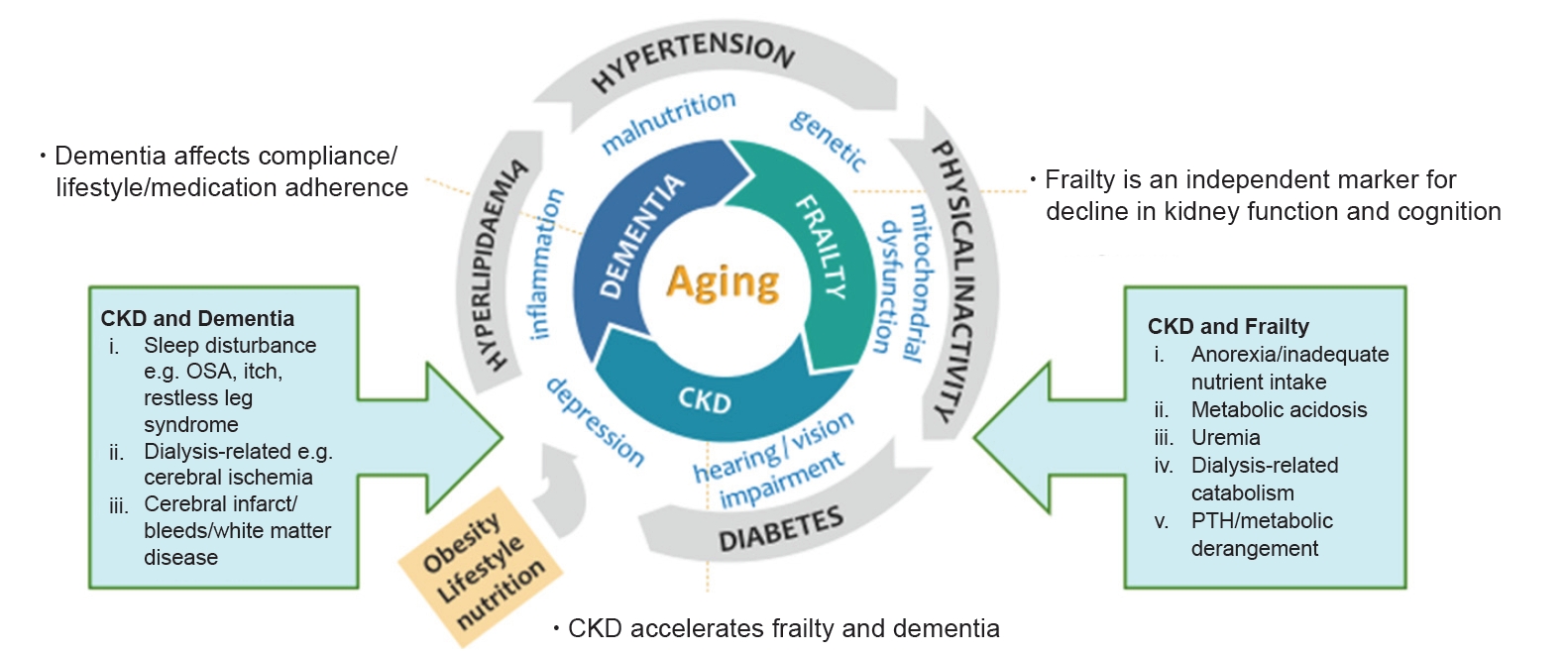
Figure 2.
Causes of anorexia associated with aging or due to CKD.
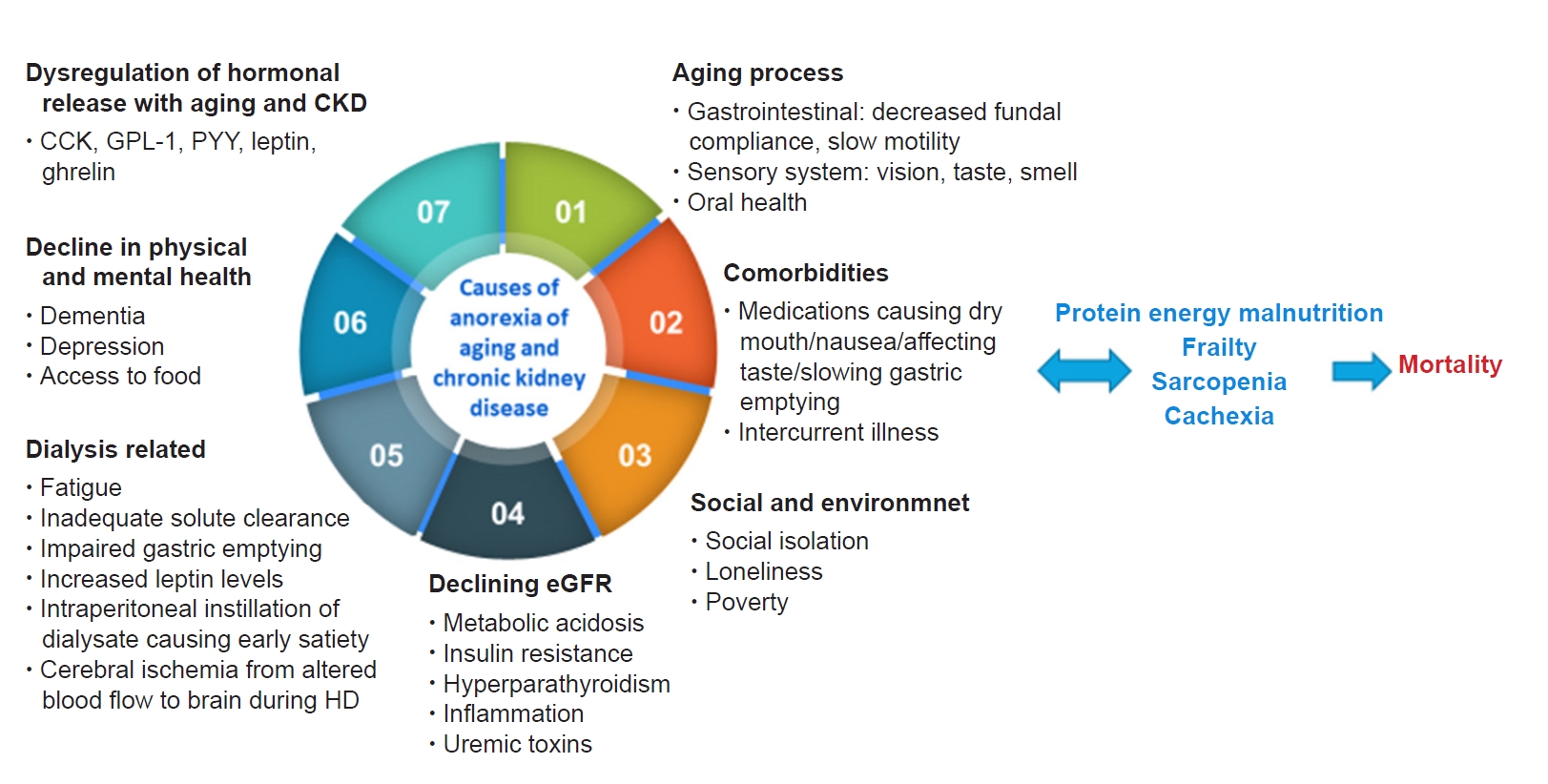
Figure 3.
Rapid geriatric assessment with an assisted management pathway.
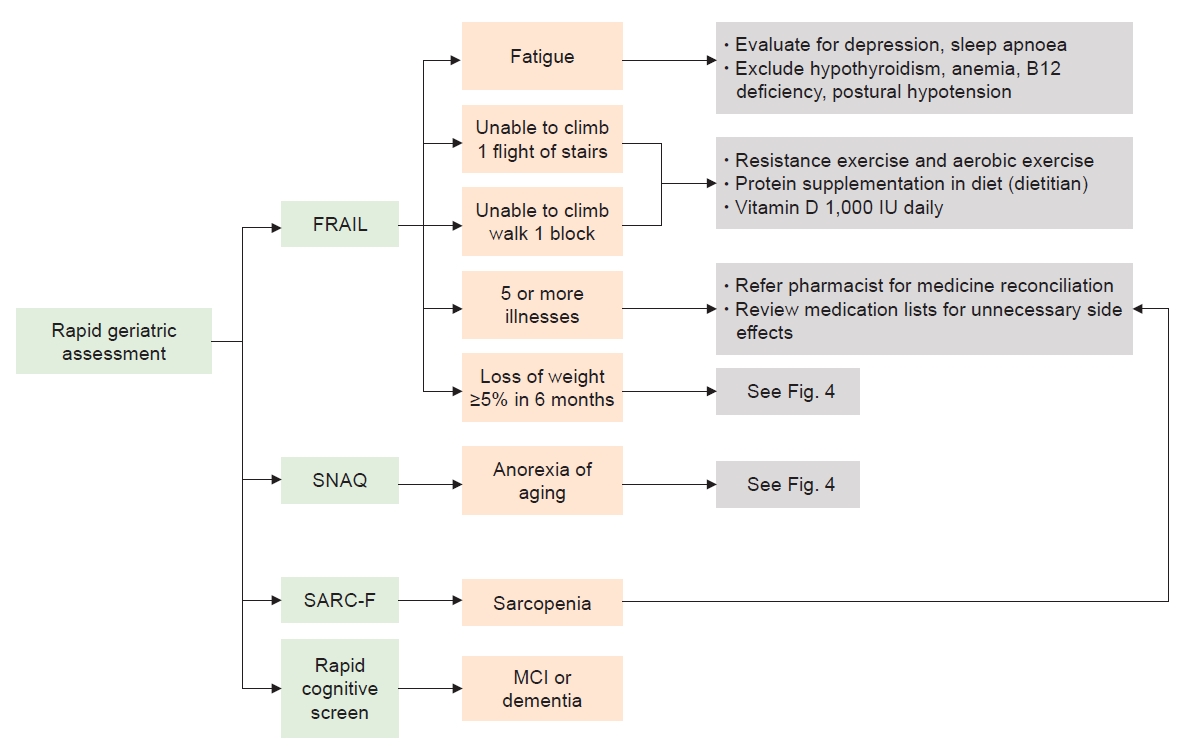
Table 1.
| Tool | Description | Estimated time (min) |
|---|---|---|
| Physical function assessment | ||
| Short physical performance battery test [31] | Measures the functional performance of the lower extremities using a set of 3 static balance tests, gait speed, and five times sit-to-stand test | ≤10 |
| Scoring: 4 points for each domain; a maximum score of 12 points | ||
| Gait speed (4, 6, or 10 m or 6 min) | Gait speed can be measured for 4, 6, or 10 m or 6 min. The 6-min gait speed test assesses endurance and aerobic capacity. Gait speed is also highly correlated with cognitive function [30,32]. Most sarcopenia guidelines use < 1 m/sec as a cutoff [33]. | ≤5 |
| Sit-to-stand (5 repetitions) | The time required to rise from the chair repeatedly 5 times. The measure of lower limb power and the ability to stand up after a fall. The cutoff for possible sarcopenia is ≥12 sec [33] and that for mobility limitation (ICOPE WHO) is >14 sec [3]. | ≤5 |
| Timed up and go [34] | Participants need to stand up from a chair unassisted, walk 3 m, turn, walk back to the chair, and sit down. | ≤5 |
| The test is used as a screening tool for falls and mobility. | ||
| Frailty assessment tool | ||
| FRAIL scale [27] | 5-Item scale assessing fatigue, resistance, ambulation, ≥5 illnesses, and loss of weight | ≤5 |
| Scoring: 1–2 points, pre-frail; 3–5 points, frail | ||
| Clinical Frailty Scale [35] | 9-Point scale ranging from very fit to severely frail to terminally ill | ≤5 |
| Fried’s Frailty Phenotype Scale [26] | 5-Item scale (requires physical measurement) assessing muscle strength, walking speed, physical activity, weight loss, and exhaustion | 5–10 |
| Scoring: 1–2 points, pre-frail; 3–5 points, frail | ||
| Rockwood Mitnitsky Frailty Index [29] | Cumulative deficits (pre-determined list) | 20–30 |
| Frailty index = number of health deficits present/number of health deficits measured | ||
| Groningen Frailty Indicator [9] | Includes 15 questions across 8 domains covering mobility, vision, hearing, nutrition, comorbidity, cognition, psychosocial, and physical fitness. The test has limited sensitivity, especially for physical fitness. | ≤10 |
| Edmonton Frail Scale [36] | Based on the following 9 components: cognition, general health, functional independence, social support, medication use, nutrition, mood, continence, and functional performance | ≤10 |
| Scoring: 0–5 points, not frail; 6–7 points, vulnerable; 8–9 points, mild frailty; 10–11 points, moderate frailty; 12–18 points, severe frailty |
Table 2.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Triage tool | |
| Informant Questionnaire on Cognitive Decline in the Elderly (IQCODE) [47,48] | 26-Item structured informant questionnaire |
| The final score is based on the ratio of total scores (26–130 points) over the total number of completed items (1–5). It is available in multiple language translations (https://nceph.anu.edu.au/research/tools-resources/informant-questionnaire-cognitive-decline-elderly). | |
| Mini-Cog [49] | Includes 3-item recall and clock-drawing (visuospatial) |
| Rapid Cognitive Screen [45] | Includes the following three items from the Veterans Affairs SLUMS examination: i) recall of five words (testing recall), ii) a clock-drawing test (testing visuospatial function), and iii) the ability to remember a story and convert the fact (testing insight and executive function) |
| Abbreviated Mental Test Score [50] | 10-Item assessment. The test is easy to administer in the ambulatory care setting. |
| Multidomain screening tool | |
| Mini-Mental State Examination [39,51] | 30-Point assessment |
| The test evaluates attention and orientation, registration, recall, memory, calculation, language, and ability to draw a complex polygon. | |
| Montreal Cognitive Assessment [39,46] | 30-Point assessment |
| The test evaluates short-term memory, visuospatial ability, executive function, attention, concentration and working memory, language, and orientation. It is available in multiple language translations (https://www.mocatest.org/about/). | |
| Saint Louis University Mental Status (SLUMS) Examination [47,52] | 30-Point assessment |
| The test evaluates attention, immediate recall and orientation, delayed recall with interference, numeric calculation and registration, memory, digit span and visuospatial and executive function. A training video and the assessment tool are available from https://www.slu.edu/medicine/internal-medicine/geriatric-medicine/aging-successfully/assessment-tools/mental-status-exam.php. | |
| Multidomain formal assessment | |
| Neuropsychological battery | Often conducted by psychologist within an acute setting |
| The test takes > 60 min and is useful for the diagnosis of dementia and/or amnestic mild cognitive impairment. |
Table 3.
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| The Council on Nutrition Appetite Questionnaire (CNAQ) [60] | Contains 8 questions related to appetite, food intake, satiety, and number of meals consumed per day derived from the AHSPQ. The total appetite score ranges from 8 (worst appetite) to 40 points (best appetite). |
| The Simplified Nutrition Assessment Questionnaire (SNAQ) [60] | Contains four questions related to appetite, food intake, satiety, and number of meals consumed per day. A total score of ≤14 points indicates a significant risk of ≥5% weight loss in the next 6 months. |
| Appetite and Diet Assessment Tool (ADAT) [61] | 44-Item self-administered questionnaire divided into three sections about appetite and eating habits in general, on dialysis, and on non-dialysis days, respectively. It takes 10 min to complete. |
| Self-assessment of appetite changes [58] | Compares present appetite vs. appetite over the last month (increased, decreased, or unchanged). |
| Subjective assessment of appetite [58] | Compares present appetite vs. appetite last week (increased, decreased, or unchanged). The test was adapted from the ADAT. |
| Visual analogue scale (VAS) [62] | Determines present appetite indicated with a line on a scale (scale extremities: 0 mm, ‘no hunger’; 100 mm, ‘hunger’). The scale is a quantitative measure of appetite. |
| Scoring: >50 mm, good appetite | |
| FAACT-ESPEN score (based on a subset of the FAACT, in particular the AC/S [63] | 12 Questions related to appetite and food intake, each of which allows for five answers (i.e., not at all, a little bit, somewhat, quite a bit, or very much). |
| The Anorexia questionnaire (AQ) [58] | Developed for the diagnosis of anorexia associated with chronic diseases, including CKD and ESRD. |
| Appetite and Food Satisfaction Questionnaire (AFSQ) [64] | Assesses the level of appetite using a facial hedonic scale and five other questions adapted from the Buckner and Dwyer tool that assesses some aspects related to food satisfaction. |
References
-
METRICS

- ORCID iDs
-
Reshma Aziz Merchant

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9032-0184Anantharaman Vathsala

https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4252-8060 - Related articles
-
The crosstalk of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and p53 in acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease
Pharmacologic therapeutics in sarcopenia with chronic kidney disease2024 March;43(2)
Urinary podocyte markers in diabetic kidney disease
Cinnamon: an aromatic condiment applicable to chronic kidney disease2023 January;42(1)



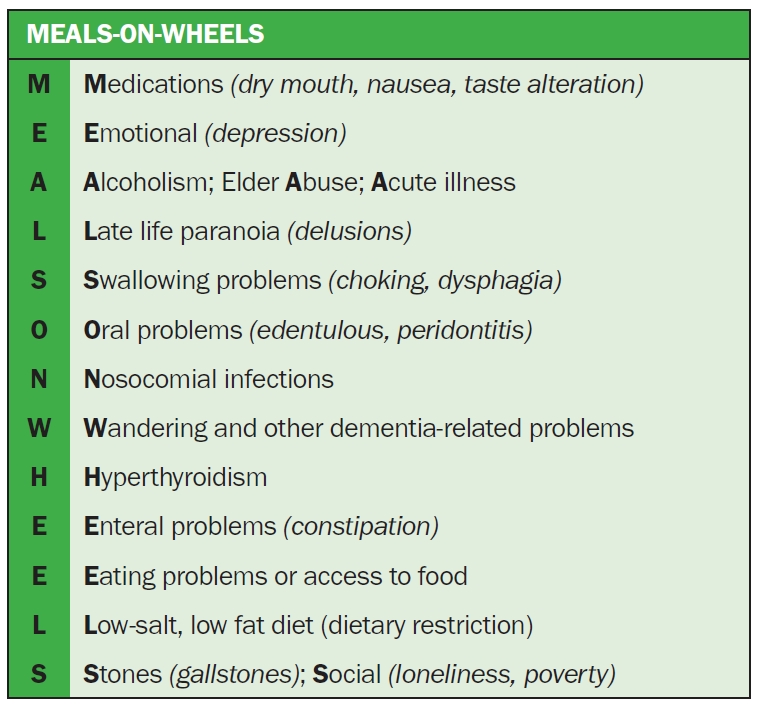
 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print















